Increased Skin Clearance and Quality of Life Improvement with Brodalumab Compared with Ustekinumab in Psoriasis Patients with Aggravating Lifestyle Factors
- PMID: 34606048
- PMCID: PMC8611142
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-021-00618-5
Increased Skin Clearance and Quality of Life Improvement with Brodalumab Compared with Ustekinumab in Psoriasis Patients with Aggravating Lifestyle Factors
Abstract
Introduction: Obesity, smoking, and alcohol consumption are prevalent in psoriasis patients and have been associated with increased disease severity and reduced treatment adherence and response. This post hoc analysis of pooled data from the phase 3 AMAGINE-2 and -3 trials compared the efficacy of brodalumab versus ustekinumab in psoriasis patients with aggravating and potentially treatment-confounding lifestyle risk factors.
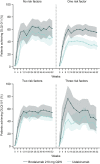
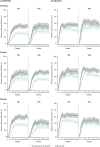
Methods: This post hoc analysis evaluated complete skin clearance, as measured by a 100% reduction of Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI100) and quality of life (QoL), as measured by a Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) score of 0/1, by the presence of risk factors (obesity, tobacco or alcohol use). A competing risk model assessed cumulative incidence over 52 weeks with outcomes of PASI100 or inadequate response.
Results: This analysis included 929 patients (brodalumab 210 mg, n = 339; ustekinumab, n = 590) with moderate-to-severe psoriasis. At week 52, odds ratios (95% confidence intervals [CIs]) for complete clearance with brodalumab versus ustekinumab were 2.50 (1.14-5.46, P = 0.0186), 4.64 (2.80-7.69, P < 0.0001), 2.06 (1.25-3.40, P = 0.0045), and 2.55 (0.55-11.91, P = 0.2117) in patients with no, one, two, or three risk factors, respectively. Corresponding odds ratios (ORs) (95% CIs) for DLQI 0/1 with brodalumab versus ustekinumab were 1.72 (0.78-3.79, P = 0.1883), 2.49 (1.54-4.02, P < 0.0002), 1.57 (0.97-2.54, P = 0.0666), and 2.07 (0.45-9.57, P = 0.3438). The 52-week cumulative incidence of patients achieving PASI100 was consistently higher for brodalumab versus ustekinumab, regardless of number of risk factors (P < 0.0001 for one or two risk factors and P = 0.0029 for three risk factors).
Conclusions: Higher levels of complete skin clearance and QoL were achieved and maintained with brodalumab versus ustekinumab in patients with moderate-to-severe psoriasis, regardless of the presence of lifestyle risk factors.
Clinical trial registration: AMAGINE-2 (NCT01708603); AMAGINE-3 (NCT01708629).
Keywords: Alcohol consumption; Brodalumab; Obesity; Psoriasis; QoL; Skin clearance; Smoking; Ustekinumab.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Krueger G, Koo J, Lebwohl M, Menter A, Stern RS, Rolstad T. The impact of psoriasis on quality of life: results of a 1998 National Psoriasis Foundation patient-membership survey. Arch Dermatol. 2001;137(3):280–284. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

