Long non-coding RNA TTN-AS1/microRNA-199a-3p/runt-related transcription factor 1 gene axis regulates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34606420
- PMCID: PMC8806903
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1982324
Long non-coding RNA TTN-AS1/microRNA-199a-3p/runt-related transcription factor 1 gene axis regulates the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
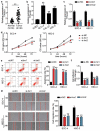
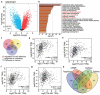
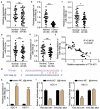
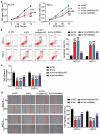
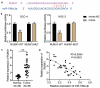
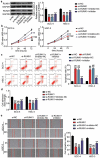
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has a high degree of malignancy, which affects the quality of life and prognosis of patients with OSCC. Our study aimed to reveal the function of long non-coding RNA TTN-AS1/microRNA-199a-3p (miR-199a-3p)/runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) axis in OSCC progression, thereby providing a novel OSCC effective strategy. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting were performed to detect the expression of TTN-AS1, miR-199a-3p, and RUNX1 in OSCC. Several cell functional experiments, including Cell Counting Kit-8, flow cytometry, and cell adhesion assays, were used to assess cell proliferation, apoptosis, adhesion, and migration. A luciferase assay was performed to confirm the interaction between TTN-AS1, miR-199a-3p, and RUNX1. Our results revealed that TTN-AS1 and RUNX1 were upregulated in OSCC tissues and cells, whereas miR-199a-3p expression was downregulated. Knockdown of TTN-AS1 or RUNX1 suppressed cell proliferation, adhesion, and migration but induced apoptosis. Additionally, miR-199a-3p inhibitor partly relieved the effects of silencing TTN-AS1 and RUNX1 in OSCC cells due to their targeting relationship. In conclusion, TTN-AS1 and RUNX1 could promote OSCC progression and miR-199a-3p partly relieved the effects of TTN-AS1 and RUNX1.
Keywords: RUNX1; TTN-AS1; miR-199a-3p; oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA BBOX1-antisense RNA 1 enhances cell proliferation and migration and suppresses apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma via the miR-3940-3p/laminin subunit gamma 2 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):11138-11153. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2059982. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35506252 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0005320 promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis by sponging microRNA-486-3p and microRNA-637.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):440-454. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2009317. Bioengineered. 2022. Retraction in: Bioengineered. 2024 Dec;15(1):2299555. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2024.2299555. PMID: 34967281 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 promotes the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma via regulating miR-338-3p/NRP1 axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109259. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109259. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31369989
-
Emerging cell cycle related non-coding RNA biomarkers from saliva and blood for oral squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Nov;50(11):9479-9496. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08791-w. Epub 2023 Sep 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37717257 Review.
-
miR-199a: A Tumor Suppressor with Noncoding RNA Network and Therapeutic Candidate in Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 31;23(15):8518. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158518. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955652 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of long noncoding RNA TTN-AS1 in various malignancies.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023 Oct;6(10):e1876. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1876. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2023. PMID: 37528740 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA PSMG3 Antisense RNA 1 is correlated with oral squamous cell carcinoma and regulates cancer cell proliferation by targeting premature microRNA-141.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Jan 15;13(1):227-235. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36777518 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA human leucocyte antigen complex group-18 HCG18 (HCG18) promoted cell proliferation and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through cyclin D1-WNT pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):9425-9434. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2060452. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35389764 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA LINC00472 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma via miR-4311/GNG7 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):6371-6382. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2040768. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35240924 Free PMC article.
-
RUNX transcription factors: biological functions and implications in cancer.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Mar 2;24(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01281-0. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38430423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chi AC, Day TA, Neville BW, Chi AC, Day TA, Neville BW . Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-an update. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(5):401–421. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
