Denatured State Conformational Biases in Three-Helix Bundles Containing Divergent Sequences Localize near Turns and Helix Capping Residues
- PMID: 34606713
- PMCID: PMC8751257
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00400
Denatured State Conformational Biases in Three-Helix Bundles Containing Divergent Sequences Localize near Turns and Helix Capping Residues
Abstract
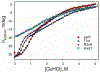
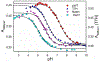
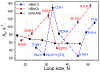
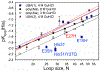
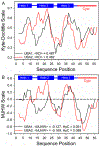
Rhodopseudomonas palustris cytochrome c', a four-helix bundle, and the second ubiquitin-associated domain, UBA(2), a three-helix bundle from the human homologue of yeast Rad23, HHR23A, deviate from random coil behavior under denaturing conditions in a fold-specific manner. The random coil deviations in each of these folds occur near interhelical turns and loops in their tertiary structures. Here, we examine an additional three-helix bundle with an identical fold to UBA(2), but a highly divergent sequence, the first ubiquitin-associated domain, UBA(1), of HHR23A. We use histidine-heme loop formation methods, employing eight single histidine variants, to probe for denatured state conformational bias of a UBA(1) domain fused to the N-terminus of iso-1-cytochrome c (iso-1-Cytc). Guanidine hydrochloride (GuHCl) denaturation shows that the iso-1-Cytc domain unfolds first, followed by the UBA(1) domain. Denatured state (4 and 6 M GuHCl) histidine-heme loop formation studies show that as the size of the histidine-heme loop increases, loop stability decreases, as expected for the Jacobson-Stockmayer relationship. However, loops formed with His35, His31, and His15, of UBA(1), are 0.6-1.1 kcal/mol more stable than expected from the Jacobson-Stockmayer relationship, confirming the importance of deviations of the denatured state from random coil behavior near interhelical turns of helical domains for facilitating folding to the correct topology. For UBA(1) and UBA(2), hydrophobic clusters on either side of the turns partially explain deviations from random coil behavior; however, helix capping also appears to be important.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

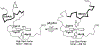
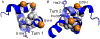

Similar articles
-
Probing Denatured State Conformational Bias in a Three-Helix Bundle, UBA(2), Using a Cytochrome c Fusion Protein.Biochemistry. 2018 Mar 20;57(11):1711-1721. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00015. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29480716
-
Effect of an Imposed Contact on Secondary Structure in the Denatured State of Yeast Iso-1-cytochrome c.Biochemistry. 2017 Dec 26;56(51):6662-6676. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01002. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 29148740 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational properties of the iso-1-cytochrome C denatured state: dependence on guanidine hydrochloride concentration.J Mol Biol. 2004 May 21;339(1):185-97. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(04)00331-6. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 15123430
-
Helical Propensity Affects the Conformational Properties of the Denatured State of Cytochrome c'.Biophys J. 2018 Jan 23;114(2):311-322. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.11.3744. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29401429 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamics of protein denatured states.Mol Biosyst. 2007 Feb;3(2):88-99. doi: 10.1039/b611895j. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Mol Biosyst. 2007. PMID: 17245488 Review.
Cited by
-
Residual Structure in the Denatured State of the Fast-Folding UBA(1) Domain from the Human DNA Excision Repair Protein HHR23A.Biochemistry. 2022 May 3;61(9):767-784. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.2c00011. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35430812 Free PMC article.
-
DMSO-Quenched H/D-Exchange 2D NMR Spectroscopy and Its Applications in Protein Science.Molecules. 2022 Jun 10;27(12):3748. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123748. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35744871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Accuracy Prediction of Stabilizing Surface Mutations to the Three-Helix Bundle, UBA(1), with EmCAST.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Oct 25;145(42):22979-22992. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c04966. Epub 2023 Oct 10. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37815921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levinthal C (1969) How to fold graciously, In Mössbaur Spectroscopy in Biological Systems (DeBrunner JTP, and Munck E, Eds.), pp 22–24, University of Illinois Press, Allerton House, Monticello, Illinois.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

