Combined Molecular and Elemental Mass Spectrometry Approaches for Absolute Quantification of Proteomes: Application to the Venomics Characterization of the Two Species of Desert Black Cobras, Walterinnesia aegyptia and Walterinnesia morgani
- PMID: 34606723
- PMCID: PMC8576837
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00608
Combined Molecular and Elemental Mass Spectrometry Approaches for Absolute Quantification of Proteomes: Application to the Venomics Characterization of the Two Species of Desert Black Cobras, Walterinnesia aegyptia and Walterinnesia morgani
Abstract
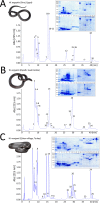
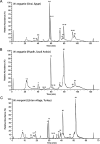
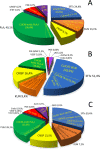
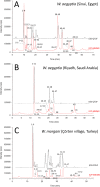
We report a novel hybrid, molecular and elemental mass spectrometry (MS) setup for the absolute quantification of snake venom proteomes shown here for two desert black cobra species within the genus Walterinnesia, Walterinnesia aegyptia and Walterinnesia morgani. The experimental design includes the decomplexation of the venom samples by reverse-phase chromatography independently coupled to four mass spectrometry systems: the combined bottom-up and top-down molecular MS for protein identification and a parallel reverse-phase microbore high-performance liquid chromatograph (RP-μHPLC) on-line to inductively coupled plasma (ICP-MS/MS) elemental mass spectrometry and electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (ESI-QToF MS). This allows to continuously record the absolute sulfur concentration throughout the chromatogram and assign it to the parent venom proteins separated in the RP-μHPLC-ESI-QToF parallel run via mass profiling. The results provide a locus-resolved and quantitative insight into the three desert black cobra venom proteome samples. They also validate the units of measure of our snake venomics strategy for the relative quantification of snake venom proteomes as % of total venom peptide bonds as a proxy for the % by weight of the venom toxins/toxin families. In a more general context, our work may pave the way for broader applications of hybrid elemental/molecular MS setups in diverse areas of proteomics.
Keywords: Walterinnesia aegyptia; Walterinnesia morgani; absolute quantification of venom proteome; combined top-down and bottom-up venomics; desert black cobra; hybrid elemental and molecular mass spectrometry; snake venomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Absolute venomics: Absolute quantification of intact venom proteins through elemental mass spectrometry.J Proteomics. 2017 Jul 5;164:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 2. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28579478
-
Identification, Characterization and Synthesis of Walterospermin, a Sperm Motility Activator from the Egyptian Black Snake Walterinnesia aegyptia Venom.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 21;21(20):7786. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207786. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33096770 Free PMC article.
-
Snake venomics - from low-resolution toxin-pattern recognition to toxin-resolved venom proteomes with absolute quantification.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018 Jul;15(7):555-568. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2018.1500904. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30005583 Review.
-
Top-down venomics of the East African green mamba, Dendroaspis angusticeps, and the black mamba, Dendroaspis polylepis, highlight the complexity of their toxin arsenals.J Proteomics. 2016 Sep 2;146:148-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.06.018. Epub 2016 Jun 16. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27318176
-
Quantification of snake venom proteomes by mass spectrometry-considerations and perspectives.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024 Sep-Oct;43(5):977-997. doi: 10.1002/mas.21850. Epub 2023 May 8. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2024. PMID: 37155340 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Technologies in Snake Venom Analysis and Applications.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 25;16(11):458. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110458. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modern venomics-Current insights, novel methods, and future perspectives in biological and applied animal venom research.Gigascience. 2022 May 18;11:giac048. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giac048. Gigascience. 2022. PMID: 35640874 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-level reference genome for the medically important Arabian horned viper (Cerastes gasperettii).Gigascience. 2025 Jan 6;14:giaf030. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaf030. Gigascience. 2025. PMID: 40478730 Free PMC article.
-
Venom characterization of the Brazilian Pampa snake Bothrops pubescens by top-down and bottom-up proteomics.Toxicon. 2022 Dec;220:106937. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2022.106937. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Toxicon. 2022. PMID: 36228757 Free PMC article.
-
Death-Leading Envenomization of Rabbits with Snake Versus Scorpion Venoms: A Comparative Forensic Investigation of Postmortem Decomposition and Beetle Succession.Insects. 2025 Jun 13;16(6):625. doi: 10.3390/insects16060625. Insects. 2025. PMID: 40559055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jenner R.; Undheim E.. Venom—The Secrets of Nature’s Deadliest Weapon; The Natural History Museum: London, U.K., 2017. ISBN 9780565094034.
-
- Van Valen L. A new evolutionary law. Evol. Theory 1973, 1, 1–30.

