Xuanfei Baidu Decoction protects against macrophages induced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway
- PMID: 34606948
- PMCID: PMC9715986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114701
Xuanfei Baidu Decoction protects against macrophages induced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway
Abstract
Ethnopharmacological relevance: Xuanfei Baidu Decoction (XFBD), one of the "three medicines and three prescriptions" for the clinically effective treatment of COVID-19 in China, plays an important role in the treatment of mild and/or common patients with dampness-toxin obstructing lung syndrome.
Aim of the study: The present work aims to elucidate the protective effects and the possible mechanism of XFBD against the acute inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis.
Methods: We use TGF-β1 induced fibroblast activation model and LPS/IL-4 induced macrophage inflammation model as in vitro cell models. The mice model of lung fibrosis was induced by BLM via endotracheal drip, and then XFBD (4.6 g/kg, 9.2 g/kg) were administered orally respectively. The efficacy and molecular mechanisms in the presence or absence of XFBD were investigated.
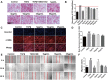
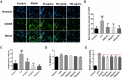
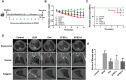
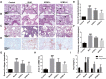
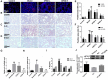
Results: The results proved that XFBD can effectively inhibit fibroblast collagen deposition, down-regulate the level of α-SMA and inhibit the migration of fibroblasts. IL-4 induced macrophage polarization was also inhibited and the secretions of the inflammatory factors including IL6, iNOS were down-regulated. In vivo experiments, the results proved that XFBD improved the weight loss and survival rate of the mice. The XFBD high-dose administration group had a significant effect in inhibiting collagen deposition and the expression of α-SMA in the lungs of mice. XFBD can reduce bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 activation and related macrophage infiltration.
Conclusions: Xuanfei Baidu Decoction protects against macrophages induced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6/STAT3; Macrophage polarization; Pulmonary fibrosis; Xuanfei baidu decoction.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Beigel J.H., Tomashek K.M., Dodd L.E., Mehta A.K., Zingman B.S., Kalil A.C., Hohmann E., Chu H.Y., Luetkemeyer A., Kline S., Lopez de Castilla D., Finberg R.W., Dierberg K., Tapson V., Hsieh L., Patterson T.F., Paredes R., Sweeney D.A., Short W.R., Touloumi G., Lye D.C., Ohmagari N., Oh M.D., Ruiz-Palacios G.M., Benfield T., Fatkenheuer G., Kortepeter M.G., Atmar R.L., Creech C.B., Lundgren J., Babiker A.G., Pett S., Neaton J.D., Burgess T.H., Bonnett T., Green M., Makowski M., Osinusi A., Nayak S., Lane H.C., Members A.-S.G. Remdesivir for the treatment of covid-19 - preliminary report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;383:1813–1826. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007764. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

