Gastrointestinal, hepatic and pancreatic manifestations of COVID-19 in children
- PMID: 34607068
- PMCID: PMC8486685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinre.2021.101818
Gastrointestinal, hepatic and pancreatic manifestations of COVID-19 in children
Abstract
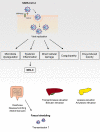
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a well-established respiratory tract pathogen. Recent studies in adults and children have shown an increasing number of patients reporting gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection such as diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. SARS-CoV-2 RNA can be detected in faeces for an extended period, even after respiratory samples have tested negative and patients are asymptomatic. However, faecal-oral transmission has not yet been proven. In this article, the latest evidence on gastrointestinal, hepato-biliary, and pancreatic manifestations in children with coronavirus disease-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome will be analysed.
Keywords: Children; Coronavirus-19; Gastrointestinal; Liver; Pancreas.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Paediatric gastrointestinal disorders in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Epidemiological and clinical implications.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 28;27(16):1716-1727. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1716. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33967552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal coronavirus disease 2019 manifestations in childhood.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2022 May 1;25(3):195-202. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000825. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2022. PMID: 35199658 Review.
-
COVID-19 extrapulmonary illness - special gastrointestinal and hepatic considerations.Dis Mon. 2020 Sep;66(9):101064. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2020.101064. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Dis Mon. 2020. PMID: 32807535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastrointestinal Perspective of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Children-An Updated Review.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021 Sep 1;73(3):299-305. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000003204. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34117195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID 19 in Children: Gastrointestinal, Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Manifestation.Mymensingh Med J. 2021 Apr;30(2):570-579. Mymensingh Med J. 2021. PMID: 33830145
Cited by
-
Liver and Pancreatic Involvement in Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Related to SARS-CoV-2: A Monocentric Study.Children (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;9(4):575. doi: 10.3390/children9040575. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455620 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Radiology of the GI Tract, Liver, and Pancreas in Patients with COVID.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2023 Mar;52(1):185-200. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2022.10.006. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 36813425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Susceptibility of SARS-CoV2 infection in children.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Nov;182(11):4851-4857. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05184-w. Epub 2023 Sep 13. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37702769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Acotiamide on Nausea as a Symptom of Chronic Nausea and Vomiting Syndrome after Coronavirus Disease 2019.Intern Med. 2023 Mar 1;62(5):739-743. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1085-22. Epub 2022 Dec 21. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 36543215 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in a Resource-Limited Center.Cureus. 2022 Feb 15;14(2):e22254. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22254. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35340456 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

