A retrospective medical chart review of clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder treated with guanfacine extended-release in routine Canadian clinical practice
- PMID: 34607580
- PMCID: PMC8491395
- DOI: 10.1186/s13034-021-00402-5
A retrospective medical chart review of clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder treated with guanfacine extended-release in routine Canadian clinical practice
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluated clinical outcomes in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) treated with the α2-adrenoceptor agonist guanfacine extended-release (GXR) in routine Canadian clinical practice.
Methods: This retrospective chart review focused on patients with ADHD aged 6-17 years initiating treatment with GXR as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy. Patients were followed for up to 12 months after GXR initiation and, if they had received prior ADHD pharmacotherapy, for 12 months before GXR initiation. The primary outcome was change in ADHD symptoms and functionality based on physician assessments, classified as improvement, no change, or worsening relative to the time of GXR initiation. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were evaluated. Clinical outcomes were also analyzed post hoc according to whether GXR treatment was received as monotherapy or adjunctive therapy, and by select psychiatric comorbidities. Exploratory analyses were conducted in patients who had received prior ADHD pharmacotherapy to evaluate clinical outcomes after initiating GXR.
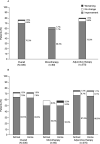
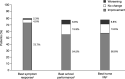
Results: Improvements in ADHD symptoms were reported for 232/330 (70.3%) patients. Functional improvements in school performance and home life were reported for 213/330 (64.5%) and 209/330 (63.3%) patients, respectively. The most frequent TEAEs (≥ 5%) were somnolence, headache, insomnia, presyncope, and decreased appetite. Improvements in ADHD symptoms were observed when GXR was received as either monotherapy (35/60 [58.3%]) or adjunctive therapy (197/270 [73.0%]). Improvements in ADHD symptoms and functionality were observed in the majority of patients with select psychiatric comorbidities. Among patients who had experienced worsening of symptoms with prior ADHD pharmacotherapy, 44/54 (81.5%) experienced symptom improvement, 33/44 (75.0%) who had previously experienced worsening of school performance improved, and 34/48 (70.8%) who had previously experienced worsening of home life improved.
Conclusion: In Canadian routine clinical practice, most children and adolescents with ADHD treated with GXR experienced improvements in ADHD symptoms and in functionality both at school and at home.
Keywords: ADHD; ADHD symptoms; Chart review; Guanfacine extended-release; Non-stimulant.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JvS has received compensation for serving as a consultant and speaker for Janssen, Purdue Pharma, and Takeda Canada Inc. JvS has also received educational grants from Janssen, Purdue Pharma, and Takeda Canada Inc., and research grants from Emalex, Janssen, Nuvelution, Purdue Pharma, Takeda Canada Inc., Biohaven and Teva. JvS has also participated in advisory boards and speaker bureaus for Janssen, Purdue Pharma, and Takeda Canada Inc. JvS owns stocks in Johnson & Johnson. SKG is an employee of Takeda Canada Inc. SKG owns stock/stock options in Takeda. CJR was an employee of Shire Pharma Canada ULC (now Takeda Canada Inc.) at the time of the study. CJR is currently an employee of Medison Canada. KH has received research grants and speaking honoraria from Takeda Canada Inc., and has acted on advisory boards and speaker bureaus for Sunovion, Janssen, Purdue, and Takeda Canada Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Visser SN, Danielson ML, Bitsko RH, Holbrook JR, Kogan MD, Ghandour RM, et al. Trends in the parent-report of health care provider-diagnosed and medicated attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: United States, 2003–2011. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(1):34–46.e32. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2013.09.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5) 5. Arlington: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

