Association of CaMK2A and MeCP2 signaling pathways with cognitive ability in adolescents
- PMID: 34607601
- PMCID: PMC8491411
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-021-00858-8
Association of CaMK2A and MeCP2 signaling pathways with cognitive ability in adolescents
Abstract
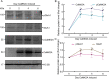
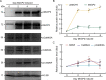
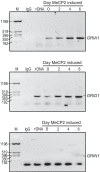
The glutamatergic signaling pathway is involved in molecular learning and human cognitive ability. Specific single variants (SNVs, formerly single-nucleotide polymorphisms) in the genes encoding N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits have been associated with neuropsychiatric disorders by altering glutamate transmission. However, these variants associated with cognition and mental activity have rarely been explored in healthy adolescents. In this study, we screened for SNVs in the glutamatergic signaling pathway to identify genetic variants associated with cognitive ability. We found that SNVs in the subunits of ionotropic glutamate receptors, including GRIA1, GRIN1, GRIN2B, GRIN2C, GRIN3A, GRIN3B, and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIα (CaMK2A) are associated with cognitive function. Plasma CaMK2A level was correlated positively with the cognitive ability of Taiwanese senior high school students. We demonstrated that elevating CaMK2A increased its autophosphorylation at T286 and increased the expression of its downstream targets, including GluA1 and phosphor- GluA1 in vivo. Additionally, methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2), a downstream target of CaMK2A, was found to activate the expression of CaMK2A, suggesting that MeCP2 and CaMK2A can form a positive feedback loop. In summary, two members of the glutamatergic signaling pathway, CaMK2A and MeCP2, are implicated in the cognitive ability of adolescents; thus, altering the expression of CaMK2A may affect cognitive ability in youth.
Keywords: Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IIα (CaMK2A); Cognitive function; Glutamatergic signaling pathway; Methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2); Single-nucleotide variant (SNV).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
De Novo Mutations in Protein Kinase Genes CAMK2A and CAMK2B Cause Intellectual Disability.Am J Hum Genet. 2017 Nov 2;101(5):768-788. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2017.10.003. Am J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 29100089 Free PMC article.
-
GABA and glutamate pathways are spatially and developmentally affected in the brain of Mecp2-deficient mice.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 25;9(3):e92169. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092169. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24667344 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear calcium signaling controls methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) phosphorylation on serine 421 following synaptic activity.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 7;287(37):30967-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.382507. Epub 2012 Jul 20. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22822052 Free PMC article.
-
Shaping synaptic plasticity: the role of activity-mediated epigenetic regulation on gene transcription.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Oct;31(6):359-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 May 9. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23665156 Review.
-
Animal model of schizophrenia: dysfunction of NMDA receptor-signaling in mice following withdrawal from repeated administration of phencyclidine.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Nov;1086:160-8. doi: 10.1196/annals.1377.003. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17185514 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and characterization of biomarkers associated with endoplasmic reticulum protein processing in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.PeerJ. 2024 Jan 2;12:e16707. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16707. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38188159 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathy: Pathogenesis of Intellectual Disability Beyond Channelopathies.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):133. doi: 10.3390/biom15010133. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative proteomics of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex reveals an early pattern of synaptic dysmaturation in children with idiopathic autism.Cereb Cortex. 2024 May 2;34(13):161-171. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae044. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38696595 Free PMC article.
-
Central Causation of Autism/ASDs via Excessive [Ca2+]i Impacting Six Mechanisms Controlling Synaptogenesis during the Perinatal Period: The Role of Electromagnetic Fields and Chemicals and the NO/ONOO(-) Cycle, as Well as Specific Mutations.Brain Sci. 2024 Apr 30;14(5):454. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14050454. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38790433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs modulate CaMKIIα/SIRT1 signaling pathway as a biomarker of cognitive ability in adolescents.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025 Feb 24;44:100970. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2025.100970. eCollection 2025 Mar. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2025. PMID: 40103671 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

