Demographic Correlates of Short-Term Mortality Among Youth and Young Adults With Youth-Onset Diabetes Diagnosed From 2002 to 2015: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
- PMID: 34607833
- PMCID: PMC8669529
- DOI: 10.2337/dc21-0728
Demographic Correlates of Short-Term Mortality Among Youth and Young Adults With Youth-Onset Diabetes Diagnosed From 2002 to 2015: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study
Abstract
Objective: To examine short-term mortality and cause of death among youth and young adults (YYAs) with youth-onset diabetes.
Research design and methods: We included 19,717 YYAs newly diagnosed with diabetes before 20 years of age from 1 January 2002 to 31 December 2015 enrolled in the SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Of these, 14,721 had type 1; 4,141 type 2; and 551 secondary and 304 other/unknown diabetes type. Cases were linked with the National Death Index through 31 December 2017. We calculated standardized mortality ratios (SMRs) and 95% CIs based on age, sex, and race/ethnicity for state and county population areas and examined underlying causes of death.
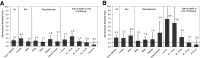
Results: During 170,148 person-years (PY) (median follow-up 8.5 years), 283 individuals died: 133 with type 1 (103.0/100,000 PY), 55 with type 2 (161.5/100,000 PY), 87 with secondary (1,952/100,000 PY), and 8 with other/unknown diabetes type (312.3/100,000 PY). SMRs (95% CI) for the first three groups were 1.5 (1.2-1.8), 2.3 (1.7-3.0), and 28.0 (22.4-34.6), respectively. Diabetes was the underlying cause of death for 42.1%, 9.1%, and 4.6% of deaths, respectively. The SMR was greater for type 2 than for type 1 diabetes (P < 0.001). SMRs were significantly higher for individuals with type 1 diabetes who were <20 years of age, non-Hispanic White and Hispanic, and female and for individuals with type 2 diabetes who were <25 years of age, from all race/ethnic minority groups, and from both sexes.
Conclusions: Excess mortality was observed among YYAs for each type of diabetes with differences in risk associated with diabetes type, age, race/ethnicity, and sex. The root causes of excess mortality among YYAs with diabetes merit further study.
© 2021 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Imperatore G, Boyle JP, Thompson TJ, et al. .; SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study Group . Projections of type 1 and type 2 diabetes burden in the U.S. population aged <20 years through 2050: dynamic modeling of incidence, mortality, and population growth. Diabetes Care 2012;35:2515–2520 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Morgan E, Cardwell CR, Black CJ, McCance DR, Patterson CC. Excess mortality in type 1 diabetes diagnosed in childhood and adolescence: a systematic review of population-based cohorts. Acta Diabetol 2015;52:801–807 - PubMed
-
- Evans-Cheung TC, Bodansky HJ, Parslow RC, Feltbower RG. Mortality and acute complications in children and young adults diagnosed with type 1 diabetes in Yorkshire, UK: a cohort study. Diabet Med 2018;35:112–120 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 DK057516/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK108173/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP002710/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006134/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006138/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP002714/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000062/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- EP-C-15-002/EPA/EPA/United States
- K23 HL148394/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- L40 HL148910/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000250/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP002708/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- HIR 10-001/HX/HSRD VA/United States
- U01 DP000247/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006131/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000248/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006136/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U01 DP000244/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- P30 DK116073/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U18 DP002709/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006133/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U18 DP006139/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000077/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK127208/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000423/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000246/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DP000254/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical