Infections due to dysregulated immunity: an emerging complication of cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 34607905
- PMCID: PMC8867274
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217260
Infections due to dysregulated immunity: an emerging complication of cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
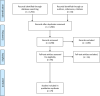
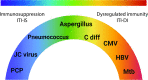
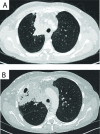
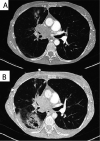
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have revolutionised cancer treatment. However, immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are a common side effect which can mimic infection. Additionally, treatment of irAEs with corticosteroids and other immunosuppressant agents can lead to opportunistic infection, which we have classed as immunotherapy infections due to immunosuppression. However, emerging reports demonstrate that some infections can be precipitated by ICIs in the absence of immunosuppressive treatment, in contrast to the majority of reported cases. These infections are characterised by a dysregulated inflammatory immune response, and so we propose they are described as immunotherapy infections due to dysregulated immunity. This review summarises the rapidly emerging evidence of these phenomena and proposes a new framework for considering infection in the context of cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: aspergillus lung disease; bacterial infection; lung cancer; lung cancer chemotherapy; opportunist lung infections; tuberculosis; viral infection.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Opportunistic infections complicating immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jun;11(6):1689-1694. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13422. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32311221 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors and infections: A particular focus on mycobacterial infections.Respir Investig. 2024 May;62(3):339-347. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2024.02.002. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Respir Investig. 2024. PMID: 38417355 Review.
-
A case report of pulmonary nocardiosis during pembrolizumab: the emerging challenge of the infections on immunotherapy.Immunotherapy. 2022 Dec;14(17):1369-1375. doi: 10.2217/imt-2022-0152. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Immunotherapy. 2022. PMID: 36420679
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated gastritis: Patterns and management.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Apr 14;30(14):1941-1948. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i14.1941. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38681126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectious complications in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Eur J Cancer. 2020 Dec;141:137-142. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.09.025. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Eur J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33137589
Cited by
-
How and when to manage respiratory infections out of hospital.Eur Respir Rev. 2022 Oct 19;31(166):220092. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0092-2022. Print 2022 Dec 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2022. PMID: 36261157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case Report: Active tuberculosis infection in CAR T-cell recipients post CAR T-cell therapy: a retrospective case series.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 May 11;13:1147454. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1147454. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37249982 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the tuberculosis granuloma: the matrix revolutions.Trends Mol Med. 2022 Feb;28(2):143-154. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2021.11.004. Epub 2021 Dec 15. Trends Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34922835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired development of memory B cells and antibody responses in humans and mice deficient in PD-1 signaling.Immunity. 2024 Dec 10;57(12):2790-2807.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.10.014. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 39603236
-
Case Report: Toripalimab: a novel immune checkpoint inhibitor in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma and severe immune-related colitis.Front Immunol. 2023 Nov 24;14:1298902. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1298902. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38077371 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
