Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency
- PMID: 34608327
- PMCID: PMC8930418
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-021-01039-7
Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency.Nat Biotechnol. 2022 Mar;40(3):432. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01175-0. Nat Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34880468 No abstract available.
Abstract
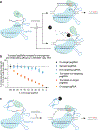
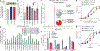
Prime editing enables the installation of virtually any combination of point mutations, small insertions or small deletions in the DNA of living cells. A prime editing guide RNA (pegRNA) directs the prime editor protein to the targeted locus and also encodes the desired edit. Here we show that degradation of the 3' region of the pegRNA that contains the reverse transcriptase template and the primer binding site can poison the activity of prime editing systems, impeding editing efficiency. We incorporated structured RNA motifs to the 3' terminus of pegRNAs that enhance their stability and prevent degradation of the 3' extension. The resulting engineered pegRNAs (epegRNAs) improve prime editing efficiency 3-4-fold in HeLa, U2OS and K562 cells and in primary human fibroblasts without increasing off-target editing activity. We optimized the choice of 3' structural motif and developed pegLIT, a computational tool to identify non-interfering nucleotide linkers between pegRNAs and 3' motifs. Finally, we showed that epegRNAs enhance the efficiency of the installation or correction of disease-relevant mutations.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors are co-inventors on patents filed by the Broad Institute on prime editing. D.R.L. is a consultant and co-founder of Prime Medicine, Beam Therapeutics, and Pairwise Plants, companies that use genome editing. A.V.A. is currently an employee of Prime Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Anzalone AV, Koblan LW & Liu DR Genome editing with CRISPR-Cas nucleases, base editors, transposases and prime editors. Nat Biotechnol 38, 824–844 (2020). - PubMed
Method References
-
- Gaudelli NM et al. Directed evolution of adenine base editors with increased activity and therapeutic application. Nat Biotechnol 38, 892–900 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Bertsimas D & Tsitsiklis J Simulated Annealing. Stat Sci 8, 10–15 (1993).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

