Effectiveness of Problem-Based Learning versus Traditional Teaching Methods in Improving Acquisition of Radiographic Interpretation Skills among Dental Students-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34608440
- PMCID: PMC8487362
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9630285
Effectiveness of Problem-Based Learning versus Traditional Teaching Methods in Improving Acquisition of Radiographic Interpretation Skills among Dental Students-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
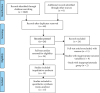
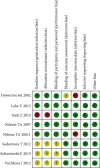
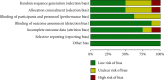
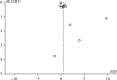
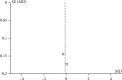
Problem-based learning is an experiential and student-centred learning method to practice important skills like querying, critical thinking, and collaboration through pair and group work. The study is aimed at comparing the effectiveness of problem-based learning (PBL) and traditional teaching (TT) methods in improving acquisition of radiographic interpretation skills among dental students. Clinical trials (randomized and nonrandomized) were conducted with the help of dental students studying oral radiology using PBL and TT methods and assessing radiographic interpretation skills, knowledge scores, and satisfaction level as outcomes. Articles published from PubMed/MEDLINE, DOAJ, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science were searched. The quality of the studies was evaluated using the Cochrane Collaboration Tool, the MINORS Checklist, and the Risk of Bias in Nonrandomized Studies of Interventions (ROBIN-I) tool. Meta-analysis was done using Review Manager 5.3. There were twenty-four articles for qualitative synthesis and 13 for meta-analysis. The cumulative mean difference was found to be 0.54 (0.18, 0.90), 4.15 (-0.35, 8.65), and -0.14 (-0.36, 0.08) for radiographic interpretation skills, knowledge scores, and satisfaction level, respectively, showing significant difference favouring PBL as compared to TT except for satisfaction level which favoured the TT group. To understand the long-term effectiveness of PBL over TT methods in oral radiology among dental students, well-designed long-term randomized controlled trials are needed.
Copyright © 2021 Alexander Maniangat Luke et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures

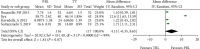

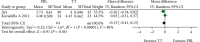
Similar articles
-
Use of problem-based learning in orthopaedics education: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Mar 8;24(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05244-1. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38459551 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Comparing hybrid problem-based and lecture learning (PBL + LBL) with LBL pedagogy on clinical curriculum learning for medical students in China: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Apr;99(16):e19687. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019687. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32311943 Free PMC article.
-
Combined administration of problem- and lecture-based learning teaching models in medical education in China: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Oct;97(43):e11366. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011366. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30412058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Emerging Teaching Models in Dental Education: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int Dent J. 2024 Dec;74(6):1185-1196. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.05.016. Epub 2024 Jul 9. Int Dent J. 2024. PMID: 38981826 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between Student Performances on Case-Based Constructed-Response Formative Assessment and Summative Assessment.J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2024 Mar 14;11:23821205241239496. doi: 10.1177/23821205241239496. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2024. PMID: 38516552 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Interactive Teaching in Online and Offline Platforms among Dental Undergraduates.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 8;19(6):3170. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063170. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35328858 Free PMC article.
-
A Prospective Comparative Analysis Regarding the Assessment of Oral Mucosal Disease Using a Validated Questionnaire to Improve the Teaching of Dental Students.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Aug 5;19(15):9663. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19159663. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35955017 Free PMC article.
-
Use of problem-based learning in orthopaedics education: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Mar 8;24(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05244-1. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38459551 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of six teaching strategies on medical students: protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2024 Jan 30;14(1):e079716. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-079716. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38296281 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADEA Commission on Change and Innovation in Dental Education, Hendricson W. D., Andrieu S. C., et al. Educational strategies associated with development of problem-solving, critical thinking, and self-directed learning. Journal of Dental Education . 2006;70(9):925–936. doi: 10.1002/j.0022-0337.2006.70.9.tb04163.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Binshabaib M., Shalabi M., Mansour S., Alageel L., Alsuwidan N., ALHarthi S. S. Role of problem-based learning in undergraduate dental education: a questionnaire-based study. Advances in Medical Education and Practice . 2019;10:79–84. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S181658. eCollection 2019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

