HIV status alters disease severity and immune cell responses in Beta variant SARS-CoV-2 infection wave
- PMID: 34608862
- PMCID: PMC8676326
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67397
HIV status alters disease severity and immune cell responses in Beta variant SARS-CoV-2 infection wave
Abstract
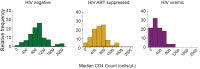
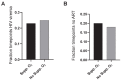
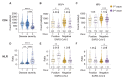
There are conflicting reports on the effects of HIV on COVID-19. Here, we analyzed disease severity and immune cell changes during and after SARS-CoV-2 infection in 236 participants from South Africa, of which 39% were people living with HIV (PLWH), during the first and second (Beta dominated) infection waves. The second wave had more PLWH requiring supplemental oxygen relative to HIV-negative participants. Higher disease severity was associated with low CD4 T cell counts and higher neutrophil to lymphocyte ratios (NLR). Yet, CD4 counts recovered and NLR stabilized after SARS-CoV-2 clearance in wave 2 infected PLWH, arguing for an interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and HIV infection leading to low CD4 and high NLR. The first infection wave, where severity in HIV negative and PLWH was similar, still showed some HIV modulation of SARS-CoV-2 immune responses. Therefore, HIV infection can synergize with the SARS-CoV-2 variant to change COVID-19 outcomes.
Keywords: COVID-19; HIV; SARS-CoV-2; antiretroviral therapy; beta variant; infectious disease; microbiology; virus.
© 2021, Karim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
FK, IG, SC, YZ, RK, MB, KK, YG, HR, NM, MM, DM, DR, TN, WH, BG, RL, EW, Td, MM, GL, AL, HK, AS No competing interests declared
Figures
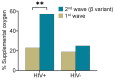





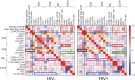

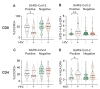
References
-
- Ambrosioni J, Blanco JL, Reyes-Urueña JM, Davies MA, Sued O, Marcos MA, Martínez E, Bertagnolio S, Alcamí J, Miro JM, Investigators C-i, COVID-19 in HIV Investigators Overview of SARS-CoV-2 infection in adults living with HIV. The Lancet HIV. 2021;8:e294–e305. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(21)00070-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Avelino-Silva VI, Miyaji KT, Mathias A, Costa DA, de Carvalho Dias JZ, Lima SB, Simoes M, Freire MS, Caiaffa-Filho HH, Hong MA, Lopes MH, Sartori AM, Kallas EG. CD4/CD8 ratio predicts yellow fever Vaccine-Induced antibody titers in Virologically suppressed HIV-Infected patients. JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes. 2016;71:189–195. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000000845. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhaskaran K, Rentsch CT, MacKenna B, Schultze A, Mehrkar A, Bates CJ, Eggo RM, Morton CE, Bacon SCJ, Inglesby P, Douglas IJ, Walker AJ, McDonald HI, Cockburn J, Williamson EJ, Evans D, Forbes HJ, Curtis HJ, Hulme WJ, Parry J, Hester F, Harper S, Evans SJW, Smeeth L, Goldacre B. HIV infection and COVID-19 death: a population-based cohort analysis of UK primary care data and linked national death registrations within the OpenSAFELY platform. The Lancet HIV. 2021;8:e24–e32. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30305-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braunstein SL, Lazar R, Wahnich A, Daskalakis DC, Blackstock OJ. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection Among People With Human Immunodeficiency Virus in New York City: A Population-Level Analysis of Linked Surveillance Data. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2021;72:e1021–e1029. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1793. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

