Protective mitochondrial fission induced by stress-responsive protein GJA1-20k
- PMID: 34608863
- PMCID: PMC8492060
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.69207
Protective mitochondrial fission induced by stress-responsive protein GJA1-20k
Abstract
The Connexin43 gap junction gene GJA1 has one coding exon, but its mRNA undergoes internal translation to generate N-terminal truncated isoforms of Connexin43 with the predominant isoform being only 20 kDa in size (GJA1-20k). Endogenous GJA1-20k protein is not membrane bound and has been found to increase in response to ischemic stress, localize to mitochondria, and mimic ischemic preconditioning protection in the heart. However, it is not known how GJA1-20k benefits mitochondria to provide this protection. Here, using human cells and mice, we identify that GJA1-20k polymerizes actin around mitochondria which induces focal constriction sites. Mitochondrial fission events occur within about 45 s of GJA1-20k recruitment of actin. Interestingly, GJA1-20k mediated fission is independent of canonical Dynamin-Related Protein 1 (DRP1). We find that GJA1-20k-induced smaller mitochondria have decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and, in hearts, provide potent protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. The results indicate that stress responsive internally translated GJA1-20k stabilizes polymerized actin filaments to stimulate non-canonical mitochondrial fission which limits ischemic-reperfusion induced myocardial infarction.
Keywords: GJA1-20k; actin dynamics; cell biology; human; ischemia/reperfusion; mitochondria; mitochondria dynamics; mouse; organ protection.
© 2021, Shimura et al.
Conflict of interest statement
DS, EN, RB, SV, SX, JW, JP, TH, JR, RS No competing interests declared
Figures

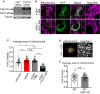
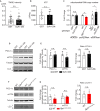
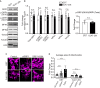
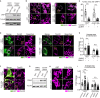




Similar articles
-
GJA1-20k and Mitochondrial Dynamics.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 23;13:867358. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.867358. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35399255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress response protein GJA1-20k promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, metabolic quiescence, and cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury.JCI Insight. 2018 Oct 18;3(20):e121900. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121900. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30333316 Free PMC article.
-
GJA1-20k Arranges Actin to Guide Cx43 Delivery to Cardiac Intercalated Discs.Circ Res. 2017 Oct 13;121(9):1069-1080. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311955. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Circ Res. 2017. PMID: 28923791 Free PMC article.
-
GJA1-20k attenuates Ang II-induced pathological cardiac hypertrophy by regulating gap junction formation and mitochondrial function.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021 Apr;42(4):536-549. doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0459-6. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021. PMID: 32620936 Free PMC article.
-
GJA1-20k, a Short Isoform of Connexin43, from Its Discovery to Its Potential Implication in Cancer Progression.Cells. 2025 Jan 24;14(3):180. doi: 10.3390/cells14030180. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DRP1, fission and apoptosis.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Apr 7;11(1):150. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02458-0. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40195359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Internal translation of Gja1 (Connexin43) to produce GJA1-20k: Implications for arrhythmia and ischemic-preconditioning.Front Physiol. 2022 Dec 7;13:1058954. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1058954. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36569758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gap Junction-Dependent and -Independent Functions of Connexin43 in Biology.Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;11(2):283. doi: 10.3390/biology11020283. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GJA1-20k and Mitochondrial Dynamics.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 23;13:867358. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.867358. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35399255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cx43-mediated hyphal folding counteracts phagosome integrity loss during fungal infection.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Sep 21;11(5):e0123823. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01238-23. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37733471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atar D, Arheden H, Berdeaux A, Bonnet JL, Carlsson M, Clemmensen P, Cuvier V, Danchin N, Dubois-Rande JL, Engblom H, Erlinge D, Firat H, Halvorsen S, Hansen HS, Hauke W, Heiberg E, Koul S, Larsen AI, Le Corvoisier P, Nordrehaug JE, Paganelli F, Pruss RM, Rousseau H, Schaller S, Sonou G, Tuseth V, Veys J, Vicaut E, Jensen SE. Effect of intravenous TRO40303 as an adjunct to primary percutaneous coronary intervention for acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction: MITOCARE study results. European Heart Journal. 2015;36:112–119. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu331. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basheer WA, Fu Y, Shimura D, Xiao S, Agvanian S, Hernandez DM, Hitzeman TC, Hong T, Shaw RM. Stress response protein GJA1-20k promotes mitochondrial biogenesis, metabolic quiescence, and cardioprotection against ischemia/reperfusion injury. JCI Insight. 2018;3:20. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121900. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

