Biomarkers in the management of acute heart failure: state of the art and role in COVID-19 era
- PMID: 34609075
- PMCID: PMC8652929
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13595
Biomarkers in the management of acute heart failure: state of the art and role in COVID-19 era
Abstract
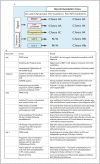
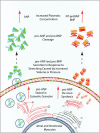
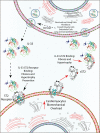
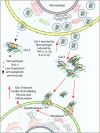
Acute heart failure (AHF) affects millions of people worldwide, and it is a potentially life-threatening condition for which the cardiologist is more often brought into play. It is crucial to rapidly identify, among patients presenting with dyspnoea, those with AHF and to accurately stratify their risk, in order to define the appropriate setting of care, especially nowadays due to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak. Furthermore, with physical examination being limited by personal protective equipment, the use of new alternative diagnostic and prognostic tools could be of extreme importance. In this regard, usage of biomarkers, especially when combined (a multimarker approach) is beneficial for establishment of an accurate diagnosis, risk stratification and post-discharge monitoring. This review highlights the use of both traditional biomarkers such as natriuretic peptides (NP) and troponin, and emerging biomarkers such as soluble suppression of tumourigenicity (sST2) and galectin-3 (Gal-3), from patients' emergency admission to discharge and follow-up, to improve risk stratification and outcomes in terms of mortality and rehospitalization.
Keywords: Acute heart failure; Biomarkers; Diagnosis; Follow-up; Mortality; Risk stratification.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

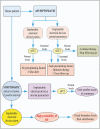
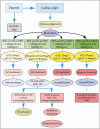
References
-
- Lippi G, Sanchis‐Gomar F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med J. 2020; 5: 15.
-
- Farmakis D, Papingiotis G, Parissis J. Acute heart failure: epidemiology and socioeconomic burden. Contin Cardiol Educ. 2017; 3: 88–92.
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JG, Coats AJ, Falk V, González‐Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016; 18: 891–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
