Immunohistochemical evaluation of D2-40, Galectin-3, Maspin and MCM7 expression in palate squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 34609416
- PMCID: PMC8597379
- DOI: 10.47162/RJME.62.1.13
Immunohistochemical evaluation of D2-40, Galectin-3, Maspin and MCM7 expression in palate squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
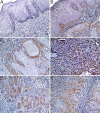
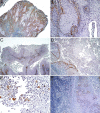
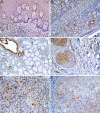
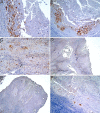
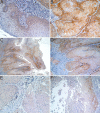
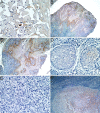
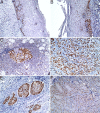
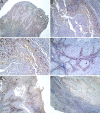
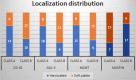
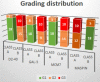
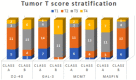
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the most frequent cancer in oral cavity and its prognosis has exhibited little improvement in the last decades. Although much less common palate SCCs manifests a higher local aggression invading very quickly the adjacent muscles and jawbones, thus being able frequently to lead to dysfunctions in chewing, swallowing, and speech. To elucidate what underlies such local aggression, we investigated the immunohistochemical expression in palate SCCs of Podoplanin (D2-40), Galectin-3 (Gal-3), mammary serine protease inhibitor (Maspin) and minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 (MCM7), markers that are known to be involved in tumor invasiveness. We found a progressive increase in reactivity for D2-40 and MCM7 from the normal epithelium toward dysplastic epithelium and respectively to SCC, which suggests the intervention of these markers in the early stages of squamous cell carcinogenesis in the palate. The highest D2-40, Gal-3 and MCM7 reactivity was observed in basaloid and in poorly differentiated (G3) palate SCCs, while for Maspin the well-differentiated (G1) palate SCCs were the most reactive. The first three markers mentioned above were most intensely expressed at the invasion front, while the Maspin reactivity was low or absent at this level. Statistically, we found significant stratification on localization, grading, muscle invasion, and survival for all investigated markers, but with very high direct correlations between D2-40, Gal-3, and MCM7 immunoreactive score (IRS) values, while between the Maspin and each of the previous markers there were very high inverse correlations. Overall, all these investigate markers proved to be responsible for the local invasiveness and regional lymph node metastasis, thus allowing a prognostic and therapeutic stratification of patients with palate SCCs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the distribution and expression of some tumor invasiveness markers in palate squamous cell carcinomas.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2020 Oct-Dec;61(4):1259-1278. doi: 10.47162/RJME.61.4.27. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2020. PMID: 34171074 Free PMC article.
-
Maspin expression in stage I and II oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Head Neck. 2001 Nov;23(11):962-6. doi: 10.1002/hed.1139. Head Neck. 2001. PMID: 11754500
-
Loss of heterozygosity in mammary serine protease inhibitor (maspin) and p53 at chromosome 17 and 18 in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma.Head Neck. 2015 Sep;37(9):1239-45. doi: 10.1002/hed.23741. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Head Neck. 2015. PMID: 24801268
-
Correlation of angiogenesis with other immunohistochemical markers in cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinomas.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2015;56(2 Suppl):665-70. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2015. PMID: 26429157
-
Maspin--a novel protease inhibitor with tumor-suppressing activity in breast cancer.Acta Oncol. 2000;39(8):931-4. doi: 10.1080/02841860050215909. Acta Oncol. 2000. PMID: 11206999 Review.
Cited by
-
The Multiple Roles of CD147 in the Development and Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An Overview.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 28;23(15):8336. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158336. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting Multi-Omics Data to Unravel Galectins as Prognostic Factors in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 27;12(3):529. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030529. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540141 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mechanism of Gorham syndrome: an update.Front Immunol. 2023 May 5;14:1165091. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165091. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37215116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Kim JW, Park Y, Roh JL, Cho KJ, Choi SH, Nam SY, Kim SY. Prognostic value of glucosylceramide synthase and P-glycoprotein expression in oral cavity cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2016;21(5):883–889. - PubMed
-
- Farhood Z, Simpson M, Ward GM, Walker RJ, Osazuwa-Peters N. Does anatomic subsite influence oral cavity cancer mortality? A SEER database analysis. Laryngoscope. 2019;129(6):1400–1406. - PubMed
-
- Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C, editors. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 8. Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) Willey-Blackwell John Wiley & Sons Ltd; 2017. pp. 272–272.
-
- Urken ML. Advances in head and neck reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 2003;113(9):1473–1476. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

