Genome-wide simple sequence repeat markers in potato: abundance, distribution, composition, and polymorphism
- PMID: 34609514
- PMCID: PMC8641542
- DOI: 10.1093/dnares/dsab020
Genome-wide simple sequence repeat markers in potato: abundance, distribution, composition, and polymorphism
Abstract
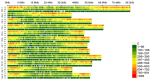
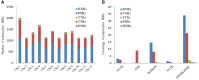
Simple sequence repeats (SSRs) are important sources of genetic diversity and are widely used as markers in genetics and molecular breeding. In this study, we examined four potato genomes of DM1-3 516 R44 (DM) from Solanum phureja, RH89039-16 (RH) from Solanum tuberosum, M6 from Solanum chacoense and Solanum commersonii to determine SSR abundance and distribution and develop a larger list of polymorphic markers for a potentially wide range of uses for the potato community. A total of 1,734,619 SSRs were identified across the four genomes with an average of 433,655 SSRs per genome and 2.31kb per SSR. The most abundant repeat units for mono-, di-, tri-, and tetra-nucleotide SSRs were (A/T)n, (AT/AT)n, (AAT/ATT)n, and (ATAT/ATAT)n, respectively. The SSRs were most abundant (78.79%) in intergenic regions and least abundant (3.68%) in untranslated regions. On average, 168,069 SSRs with unique flanking sequences were identified in the four genomes. Further, we identified 16,245 polymorphic SSR markers among the four genomes. Experimental validation confirmed 99.69% of tested markers could generate target bands. The high-density potato SSR markers developed in this study will undoubtedly facilitate the application of SSR markers for genetic research and marker-pyramiding in potato breeding.
Keywords: markers; polymorphism; potato; simple sequence repeat; whole-genome sequence.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Kazusa DNA Research Institute. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Development and characterization of simple sequence repeat markers providing genome-wide coverage and high resolution in maize.DNA Res. 2013 Oct;20(5):497-509. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dst026. Epub 2013 Jun 26. DNA Res. 2013. PMID: 23804557 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of genetic diversity among Indian potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) collection using microsatellite and retrotransposon based marker systems.Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014 Apr;73:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014. PMID: 24440815
-
Analysis of the genetic composition of anther-derived potato by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA and simple sequence repeats.Genome. 1995 Dec;38(6):1153-62. doi: 10.1139/g95-153. Genome. 1995. PMID: 8654912
-
Pattern and variation in simple sequence repeat (SSR) at different genomic regions and its implications to maize evolution and breeding.BMC Genomics. 2023 Mar 21;24(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09156-0. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36944913 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of highly informative and user-friendly microsatellites (SSRs) for genotyping of cultivated potato.Theor Appl Genet. 2004 Mar;108(5):881-90. doi: 10.1007/s00122-003-1494-7. Epub 2003 Nov 27. Theor Appl Genet. 2004. PMID: 14647900
Cited by
-
Repeat-mediated recombination results in Complex DNA structure of the mitochondrial genome of Trachelospermum jasminoides.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Oct 16;24(1):966. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05568-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39407117 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Editing Sites Identification and Multi-Elements Association Analysis in Camellia sinensis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15317. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015317. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894996 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and evolutionary comparative analysis of the DIR gene family in Nicotiana tabacum L. and Solanum tuberosum L.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 5;25(1):671. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10577-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38970011 Free PMC article.
-
De Novo Hybrid Assembly of the Tripterygium wilfordii Mitochondrial Genome Provides the Chromosomal Mitochondrial DNA Structure and RNA Editing Events.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 23;26(15):7093. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157093. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806225 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Microsatellites in the Akebia trifoliata Genome and Their Transferability and Development of a Whole Set of Effective, Polymorphic, and Physically Mapped Simple Sequence Repeat Markers.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 18;13:860101. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.860101. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35371184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCouch S.R., Teytelman L., Xu Y., et al.2002, Development and mapping of 2240 new SSR markers for rice, DNA Res., 9, 199–207. - PubMed
-
- Nicot N., Chiquet V., Gandon B., et al.2004, Study of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from wheat expressed sequence tags (ESTs), Theor. Appl. Genet., 109, 800–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

