Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition as an Emerging Therapy in Systemic Autoimmune Disease
- PMID: 34609725
- PMCID: PMC8491186
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-021-01592-0
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition as an Emerging Therapy in Systemic Autoimmune Disease
Abstract
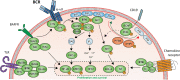
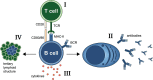
Systemic autoimmune disorders are complex heterogeneous chronic diseases involving many different immune cells. A significant proportion of patients respond poorly to therapy. In addition, the high burden of adverse effects caused by "classical" anti-rheumatic or immune modulatory drugs provides a need to develop more specific therapies that are better tolerated. Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a crucial signaling protein that directly links B-cell receptor (BCR) signals to B-cell activation, proliferation, and survival. BTK is not only expressed in B cells but also in myeloid cells, and is involved in many different signaling pathways that drive autoimmunity. This makes BTK an interesting therapeutic target in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. The past decade has seen the emergence of first-line BTK small-molecule inhibitors with great efficacy in the treatment of B-cell malignancies, but with unfavorable safety profiles for use in autoimmunity due to off-target effects. The development of second-generation BTK inhibitors with superior BTK specificity has facilitated the investigation of their efficacy in clinical trials with autoimmune patients. In this review, we discuss the role of BTK in key signaling pathways involved in autoimmunity and provide an overview of the different inhibitors that are currently being investigated in clinical trials of systemic autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, as well as available results from completed trials.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Corneth OBJ, Klein Wolterink RGJ, Hendriks RW. BTK Signaling in B cell differentiation and autoimmunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;393:67–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

