Demographic and Clinical Outcomes of Brazilian Patients With Stage III or IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Evidence Study on the Basis of Deterministic Linkage Approach
- PMID: 34609902
- PMCID: PMC8492375
- DOI: 10.1200/GO.21.00228
Demographic and Clinical Outcomes of Brazilian Patients With Stage III or IV Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Real-World Evidence Study on the Basis of Deterministic Linkage Approach
Abstract
Purpose: Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type of lung cancer and accounts for 80%-90% of the cases. In Brazil, between 2018 and 2019, lung cancer was ranked as the second most frequent cancer among men and the fourth among women. The primary objectives were to describe the journey and survival rates of patients with advanced NSCLC treated in the Brazilian private health care system (HCS).
Materials and methods: A retrospective cohort study was based on the search in administrative databases to analyze the Brazilian private HCS. Patients with advanced NSCLC diagnosed between 2011 and 2016 were included. The data on demographics, cancer-related information, treatment-related information, and resources used were collected. Survival analyses were performed using the semiparametric Kaplan-Meier method to assess mortality by NSCLC stage, with NSCLC diagnosis as the index date.
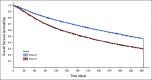
Results: A total of 5,016 patients were included. Most patients were between 60 and 69 years old (33.6%) and had completed elementary school (52.2%). There was a greater proportion of men (58.1% v 41.9%), and the majority of patients had stage IV NSCLC (67%). It took an average of 31 days, from the first consultation, to have diagnosis. In 44% of the cases, a clinical oncologist was the first specialist in the HCS that the patient was referred to. After the diagnosis, the median time to start of treatment was 35 days. Chemotherapy alone was the most common treatment regimen (32%). The median overall survival was 11.5 months and 6 months for stage II and IV NSCLC, respectively.
Conclusion: This study provides contemporary data on stage III and IV NSCLC in private health care in Brazil, which has shown a high rate of metastatic disease diagnoses, high health care-related costs, and low survival rates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization : Cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer
-
- Instituto Nacional de Câncer : Estimativa 2018: incidência de câncer no Brasil. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Instituto Nacional de Câncer José Alencar Gomes da Silva, 2017. https://rbc.inca.gov.br/revista/index.php/revista/article/view/115
-
- American Cancer Society : What Is Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer? https://www.cancer.org/cancer/non-small-cell-lung-cancer/about/what-is-n...
-
- ESMO : Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Guide for Patients. https://www.esmo.org/Patients/Patient-Guides/Non-Small-Cell-Lung-Cancer
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical