Differentiation of brain metastases originating from lung and breast cancers using apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis and the relation of histogram parameters with Ki-67
- PMID: 34609916
- PMCID: PMC9244744
- DOI: 10.1177/19714009211049082
Differentiation of brain metastases originating from lung and breast cancers using apparent diffusion coefficient histogram analysis and the relation of histogram parameters with Ki-67
Abstract
Purpose: A fast, reliable and non-invasive method is required in differentiating brain metastases (BMs) originating from lung cancer (LC) and breast cancer (BC). The aims of this study were to assess the role of histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps in differentiating BMs originated from LC and BC, and then to investigate further the association of ADC histogram parameters with Ki-67 index in BMs.
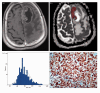
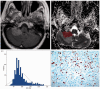
Methods: A total of 55 patients (LC, N = 40; BC, N = 15) with BMs histopathologically confirmed were enrolled in the study. The LC group was divided into small-cell lung cancer (SCLC; N = 15) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC; N = 25) groups. ADC histogram parameters (ADCmax, ADCmean, ADCmin, ADCmedian, ADC10, ADC25, ADC75 and ADC90, skewness, kurtosis and entropy) were derived from ADC maps. Mann-Whitney U-test, independent samples t-test, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis and Spearman correlation analysis were used for statistical assessment.
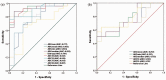
Results: ADC histogram parameters did not show significant differences between LC and BC groups (p > 0.05). Subgroup analysis showed that various ADC histogram parameters were found to be statistically lower in the SCLC group compared to the NSCLC and BC groups (p < 0.05). ROC analysis showed that ADCmean and ADC10 for differentiating SCLC BMs from NSCLC, and ADC25 for differentiating SCLC BMs from BC achieved optimal diagnostic performances. Various histogram parameters were found to be significantly correlated with Ki-67 (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Histogram analysis of ADC maps may reflect tumoural proliferation potential in BMs and can be useful in differentiating SCLC BMs from NSCLC and BC BMs.
Keywords: Brain metastases; apparent diffusion coefficient; breast cancer; histogram analysis; lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gavrilovic IT, Posner JB. Brain metastases: epidemiology and pathophysiology. J Neurooncol 2005; 75: 5–14. - PubMed
-
- Soffietti R, Cornu P, Delattre JY, et al. EFNS guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of brain metastases: report of an EFNS Task Force. Eur J Neurol 2006; 13: 674–681. - PubMed
-
- Nayak L, Lee EQ, Wen PY. Epidemiology of brain metastases. Curr Oncol Rep 2012; 14: 48–54. - PubMed
-
- Scholzen T, Gerdes J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 2000; 182: 311–322. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

