Does optimized adherence support improve treatment outcomes in RR / MDR-TB patients on 18-20 months regimen in Tbilisi, Georgia?
- PMID: 34609958
- PMCID: PMC9323534
- DOI: 10.3855/jidc.13783
Does optimized adherence support improve treatment outcomes in RR / MDR-TB patients on 18-20 months regimen in Tbilisi, Georgia?
Abstract
Introduction: Adherence to second-line antituberculosis drug is challenging. A combination of strategies needs to be implemented to achieve adherence. In Georgia an optimized adherence support (OAS) - a package of education, psychosocial support and adherence counselling - was added to the already existing package of adherence support (supervised treatment, adherence incentives, transport cost reimbursement) to improve adherence and increase treatment success. We assessed the additive benefits of OAS on adherence and treatment outcomes.
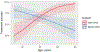
Methodology: This was a before and after cohort study using routine programme data in the National Center for Tuberculosis and Lung Diseases in Tbilisi. All adult rifampicin- and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (RR/MDR-TB) patients enrolled for treatment under directly observed therapy in the NCTLD during the period before (June 2015 - January 2016) and after (June 2017 - January 2018) were included in the study. Primary outcomes were: i) adequate adherence defined as ≥ 85% of days covered by TB medication during the whole treatment period; ii) final treatment outcomes.
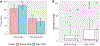
Results: Of 221 RR/MDR-TB, most patients were male (76%, N = 167) with a mean age of 41 ± 14 years. Adherence data was available for 111 patients in the 'before' and 97 patients in the 'after' cohort. Adequate adherence was achieved by 62% (69/111) in the 'before' and 70% (68/97) in the 'after' cohort (p = 0.290). Overall treatment success was 64% (73/114) and 63% (67/107) in the 'before' and 'after' cohorts respectively (p = 0.937).
Conclusions: Implementation of OAS had modest effect on adherence and had no additive benefits on treatment outcomes among RR/MDR-TB patients on 18-20 months regimen.
Keywords: SORT IT; adherence; before-and-after study; drug-resistant tuberculosis; treatment outcomes.
Copyright (c) 2021 Tinatin Jomidava, Mohammed Khogali, Yuliia Sereda, Zaza Avaliani, Malkhaz Davitashvili, Mikheil Madzgharashvili, Nestan Tukvadze, Lali Chaphurishvili, Mamuka Chincharauli, Maia Kipiani.
Conflict of interest statement
No Conflict of Interest is declared
Figures
References
-
- Dheda K, Gumbo T, Maartens G, Dooley KE, McNerney R, Murray M, Furin J, Nardell EA, London L, Lessem E, Theron G, van Helden P, Niemann S, Merker M, Dowdy D, Van Rie A, Siu GK, Pasipanodya JG, Rodrigues C, Clark TG, Sirgel FA, Esmail A, Lin HH, Atre SR, Schaaf HS, Chang KC, Lange C, Nahid P, Udwadia ZF, Horsburgh CR Jr, Churchyard GJ, Menzies D, Hesseling AC, Nuermberger E, McIlleron H, Fennelly KP, Goemaere E, Jaramillo E, Low M, Jara CM, Padayatchi N, Warren RM (2017) The epidemiology, pathogenesis, transmission, diagnosis, and management of multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant, and incurable tuberculosis. Lancet Respir Med S2213–2600: 30079–6. - PubMed
-
- Law S, Daftary A, O’Donnell M, Padayatchi N, Calzavara L, Menzies D (2019) Interventions to improve retention-in-care and treatment adherence among patients with drug-resistant tuberculosis: A systematic review. Eur Respir J. 53: 1801030. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2019) Global Tuberculosis Report 2019. Geneva, Switzerland. Available: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/329368/9789241565714-en.... Accessed 27 August 2020.
