The TGF-β/HDAC7 axis suppresses TCA cycle metabolism in renal cancer
- PMID: 34609963
- PMCID: PMC8663777
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.148438
The TGF-β/HDAC7 axis suppresses TCA cycle metabolism in renal cancer
Abstract
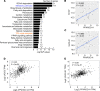
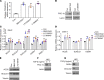
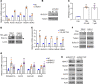
Mounting evidence points to alterations in mitochondrial metabolism in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, the mechanisms that regulate the TCA cycle in RCC remain uncharacterized. Here, we demonstrate that loss of TCA cycle enzyme expression is retained in RCC metastatic tissues. Moreover, proteomic analysis demonstrates that reduced TCA cycle enzyme expression is far more pronounced in RCC relative to other tumor types. Loss of TCA cycle enzyme expression is correlated with reduced expression of the transcription factor PGC-1α, which is also lost in RCC tissues. PGC-1α reexpression in RCC cells restores the expression of TCA cycle enzymes in vitro and in vivo and leads to enhanced glucose carbon incorporation into TCA cycle intermediates. Mechanistically, TGF-β signaling, in concert with histone deacetylase 7 (HDAC7), suppresses TCA cycle enzyme expression. Our studies show that pharmacologic inhibition of TGF-β restores the expression of TCA cycle enzymes and suppresses tumor growth in an orthotopic model of RCC. Taken together, this investigation reveals a potentially novel role for the TGF-β/HDAC7 axis in global suppression of TCA cycle enzymes in RCC and provides insight into the molecular basis of altered mitochondrial metabolism in this malignancy.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell Biology; Mitochondria; Molecular biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

