Diverse sediment microbiota shape methane emission temperature sensitivity in Arctic lakes
- PMID: 34611153
- PMCID: PMC8492752
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25983-9
Diverse sediment microbiota shape methane emission temperature sensitivity in Arctic lakes
Abstract
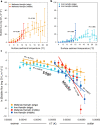
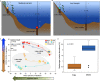
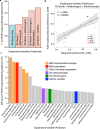
Northern post-glacial lakes are significant, increasing sources of atmospheric carbon through ebullition (bubbling) of microbially-produced methane (CH4) from sediments. Ebullitive CH4 flux correlates strongly with temperature, reflecting that solar radiation drives emissions. However, here we show that the slope of the temperature-CH4 flux relationship differs spatially across two post-glacial lakes in Sweden. We compared these CH4 emission patterns with sediment microbial (metagenomic and amplicon), isotopic, and geochemical data. The temperature-associated increase in CH4 emissions was greater in lake middles-where methanogens were more abundant-than edges, and sediment communities were distinct between edges and middles. Microbial abundances, including those of CH4-cycling microorganisms and syntrophs, were predictive of porewater CH4 concentrations. Results suggest that deeper lake regions, which currently emit less CH4 than shallower edges, could add substantially to CH4 emissions in a warmer Arctic and that CH4 emission predictions may be improved by accounting for spatial variations in sediment microbiota.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wik M, Varner RK, Anthony KW, MacIntyre S, Bastviken D. Climate-sensitive northern lakes and ponds are critical components of methane release. Nat. Geosci. 2016;9:99–105. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2578. - DOI
-
- Wik M, et al. Energy input is primary controller of methane bubbling in subarctic lakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014;41:555–560. doi: 10.1002/2013GL058510. - DOI
-
- Holgerson MA, Raymond PA. Large contribution to inland water CO2 and CH4 emissions from very small ponds. Nat. Geosci. 2016;9:222–226. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2654. - DOI
-
- Tan Z, Zhuang Q. Arctic lakes are continuous methane sources to the atmosphere under warming conditions. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015;10:054016. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/10/5/054016. - DOI
-
- Verpoorter C, Kutser T, Seekell DA, Tranvik LJ. A global inventory of lakes based on high-resolution satellite imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014;41:6396–6402. doi: 10.1002/2014GL060641. - DOI

