Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells
- PMID: 34611326
- PMCID: PMC8491763
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells
Abstract
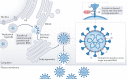
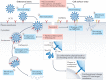
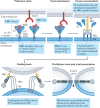
The unprecedented public health and economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has been met with an equally unprecedented scientific response. Much of this response has focused, appropriately, on the mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells, and in particular the binding of the spike (S) protein to its receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and subsequent membrane fusion. This Review provides the structural and cellular foundations for understanding the multistep SARS-CoV-2 entry process, including S protein synthesis, S protein structure, conformational transitions necessary for association of the S protein with ACE2, engagement of the receptor-binding domain of the S protein with ACE2, proteolytic activation of the S protein, endocytosis and membrane fusion. We define the roles of furin-like proteases, transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2) and cathepsin L in these processes, and delineate the features of ACE2 orthologues in reservoir animal species and S protein adaptations that facilitate efficient human transmission. We also examine the utility of vaccines, antibodies and other potential therapeutics targeting SARS-CoV-2 entry mechanisms. Finally, we present key outstanding questions associated with this critical process.
© 2021. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lan J, et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature. 2020;581:215–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

