Interleukin-17 family members in health and disease
- PMID: 34611705
- PMCID: PMC8633656
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxab075
Interleukin-17 family members in health and disease
Abstract
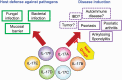
The interleukin-17 (IL-17) family consists of six family members (IL-17A-IL-17F) and all the corresponding receptors have been identified recently. This family is mainly involved in the host defense mechanisms against bacteria, fungi and helminth infection by inducing cytokines and chemokines, recruiting neutrophils, inducing anti-microbial proteins and modifying T-helper cell differentiation. IL-17A and some other family cytokines are also involved in the development of psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis by inducing inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, and antibodies against IL-17A as well as the receptor IL-17RA are being successfully used for the treatment of these diseases. Involvement in the development of inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis and tumors has also been suggested in animal disease models. In this review, we will briefly review the mechanisms by which IL-17 cytokines are involved in the development of these diseases and discuss possible treatment of inflammatory diseases by targeting IL-17 family members.
Keywords: IL-17 family; IL-17 receptor; antibodies against IL-17 and the receptors; autoimmune disease; psoriasis.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japanese Society for Immunology.
Figures
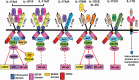
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

