Graves' disease associated with HIV disease and late immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome following the initiation of antiretroviral therapy
- PMID: 34612207
- PMCID: PMC8558905
- DOI: 10.1530/EDM-21-0094
Graves' disease associated with HIV disease and late immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome following the initiation of antiretroviral therapy
Abstract
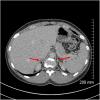
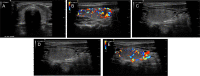
Summary: Both human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and antiretroviral therapy (ART) are associated with endocrine dysfunction (1). The term 'immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome' (IRIS) describes an array of inflammatory conditions that occur during the return of cell-mediated immunity following ART. Graves' disease (GD) occurs rarely as an IRIS following ART. In this study, we describe the case of a 40-year-old Brazilian female who was diagnosed with HIV following admission with cryptococcal meningitis and salmonellosis. At this time, she was also diagnosed with adrenal insufficiency. Her CD4 count at diagnosis was 17 cells/µL which rose to 256 cells/µL over the first 3 months of ART. Her HIV viral load, however, consistently remained detectable. When viral suppression was finally achieved 21 months post diagnosis, an incremental CD4 count of 407 cells/µL over the following 6 months ensued. Subsequently, she was diagnosed with a late IRIS to cryptococcus 32 months following initial ART treatment, which manifested as non-resolving lymphadenitis and resolved with high-dose steroids. Following the initiation of ART for 45 months, she developed symptomatic Graves' hyperthyroidism. At this time, her CD4 count had risen to 941 cells/µL. She has been rendered euthyroid on carbimazole. This case serves to remind us that GD can occur as an IRIS post ART and typically has a delayed presentation.
Learning points: Endocrinologists should be aware of the endocrine manifestations of HIV disease, in particular, thyroid pathology. Endocrinologists should be aware that IRIS can occur following the initiation of ART. Thyroid dysfunction can occur post ART of which Graves' disease (GD) is the most common thyroid manifestation. GD as a manifestation of ART-induced IRIS can have a delayed presentation. Infectious disease physicians should be aware of endocrine manifestations associated with HIV and ART.
Figures

References
-
- Chen F, Day SL, Metcalfe RA, Sethi G, Kapembwa MS, Brook MG, Churchill D, de Ruiter A, Robinson S, Lacey CJet al.Characteristics of autoimmune thyroid disease occurring as a late complication of immune reconstitution in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) disease. Medicine 20058498–106. (10.1097/01.md.0000159082.45703.90) - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

