A rapid and low-cost protocol for the detection of B.1.1.7 lineage of SARS-CoV-2 by using SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR
- PMID: 34613565
- PMCID: PMC8493944
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-021-06717-y
A rapid and low-cost protocol for the detection of B.1.1.7 lineage of SARS-CoV-2 by using SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR
Erratum in
-
Correction to: A rapid and low‑cost protocol for the detection of B.1.1.7 lineage of SARS‑CoV‑2 by using SYBR Green‑based RT‑qPCR.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Apr;49(4):3365. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-07086-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34977991 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The new SARS-CoV-2 variant VOC (202012/01), identified recently in the United Kingdom (UK), exhibits a higher transmissibility rate compared to other variants, and a reproductive number 0.4 higher. In the UK, scientists were able to identify the increase of this new variant through the rise of false negative results for the spike (S) target using a three-target RT-PCR assay (TaqPath kit).
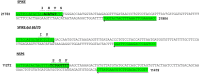
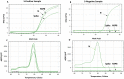
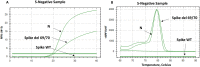
Methods: To control and study the current coronavirus pandemic, it is important to develop a rapid and low-cost molecular test to identify the aforementioned variant. In this work, we designed primer sets specific to the VOC (202012/01) to be used by SYBR Green-based RT-PCR. These primers were specifically designed to confirm the deletion mutations Δ69/Δ70 in the spike and the Δ106/Δ107/Δ108 in the NSP6 gene. We studied 20 samples from positive patients, detected by using the Applied Biosystems TaqPath RT-PCR COVID-19 kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA) that included the ORF1ab, S, and N gene targets. 16 samples displayed an S-negative profile (negative for S target and positive for N and ORF1ab targets) and four samples with S, N and ORF1ab positive profile.
Results: Our results emphasized that all S-negative samples harbored the mutations Δ69/Δ70 and Δ106/Δ107/Δ108. This protocol could be used as a second test to confirm the diagnosis in patients who were already positive to COVID-19 but showed false negative results for S-gene.
Conclusions: This technique may allow to identify patients carrying the VOC (202012/01) or a closely related variant, in case of shortage in sequencing.
Keywords: B.1.1.7 lineage; COVID-19 pandemic; SARS CoV-2; SYBR Green-based RT-PCR; VOC (202012/01).
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variant by SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 Apr 27;9(1):bpae020. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae020. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38680163 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of analytical sensitivity and efficiency for SARS-CoV-2 primer sets by TaqMan-based and SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Mar;106(5-6):2207-2218. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11822-4. Epub 2022 Feb 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35218386 Free PMC article.
-
Real-Time RT-PCR Allelic Discrimination Assay for Detection of N501Y Mutation in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with B.1.1.7 Variant of Concern.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0068121. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00681-21. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35170989 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of SARS-CoV-2 and techniques of diagnosis and surveillance.Adv Clin Chem. 2024;118:35-85. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2023.11.003. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Adv Clin Chem. 2024. PMID: 38280807 Review.
-
The Significance and Importance of dPCR, qPCR, and SYBR Green PCR Kit in the Detection of Numerous Diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(3):169-179. doi: 10.2174/0113816128276560231218090436. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38243947 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a simple genotyping method based on indel mutations to rapidly screen SARS-CoV-2 circulating variants: Delta, Omicron BA.1 and BA.2.J Virol Methods. 2022 Sep;307:114570. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2022.114570. Epub 2022 Jun 18. J Virol Methods. 2022. PMID: 35724698 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variant by SYBR Green-based RT-qPCR.Biol Methods Protoc. 2024 Apr 27;9(1):bpae020. doi: 10.1093/biomethods/bpae020. eCollection 2024. Biol Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38680163 Free PMC article.
-
Obtaining Reliable RT-qPCR Results in Molecular Diagnostics-MIQE Goals and Pitfalls for Transcriptional Biomarker Discovery.Life (Basel). 2022 Mar 7;12(3):386. doi: 10.3390/life12030386. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35330136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specific allelic discrimination of N501Y and other SARS-CoV-2 mutations by ddPCR detects B.1.1.7 lineage in Washington State.J Med Virol. 2021 Oct;93(10):5931-5941. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27155. Epub 2021 Jul 3. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 34170525 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: BA.1 subvariant showing a BA.2-like pattern using a variant-specific PCR assay due to a single point mutation downstream the spike 69/70 deletion.Virol J. 2022 Oct 27;19(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01883-2. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 36303187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lopez-Rincon A, Alberto T, Lucero MM, Eric C et al (2020) Design of specific primer set for detection of B. 1.1. 7 SARS-CoV-2 variant using deep learning. bioRxiv. 10.1101/2020.12.29.424715
-
- Erik V, Swapnil M, Meera C, Jeffrey CB, Robert J, Lily G, et al (2020) Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B. 1.1. 7 in England: insights from linking epidemiological and genetic data. medRxiv. 10.1101/2020.12.30.20249034
-
- Meera C, Susan H, Gavin D, Hester A, Theresa L, Obaghe E et al (2020) Investigation of novel SARS-COV-2 variant: variant of concern 202012/01. Public Health England. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/investigation-of-novel-sars-c...
-
- Andrew R, Nick L, Oliver P, Wendy B, Jeff B, Alesandro C et al (2020) Preliminary genomic characterisation of an emergent SARS-CoV-2 lineage in the UK defined by a novel set of spike mutations: COVID-19 genomics UK Consortium. https://virological.org/t/preliminary-genomic-characterisation-of-an-eme...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

