Agreement between local and central reading of endoscopic disease activity in ulcerative colitis: results from the tofacitinib OCTAVE trials
- PMID: 34614208
- PMCID: PMC9291991
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.16626
Agreement between local and central reading of endoscopic disease activity in ulcerative colitis: results from the tofacitinib OCTAVE trials
Abstract
Background: Endoscopy is routine in trials of ulcerative colitis therapies.
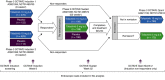
Aim: To investigate agreement between central and local Mayo endoscopic subscore (MES) reads in the OCTAVE programme METHODS: Flexible sigmoidoscopy was performed in tofacitinib induction (OCTAVE Induction 1&2, NCT01465763 and NCT01458951), maintenance (OCTAVE Sustain, NCT01458574) and open-label, long-term extension (OCTAVE Open, NCT01470612) studies. Kappa statistics and Bowker's tests evaluated agreement/disagreement between centrally and locally read MES, with potential determinants of differences analysed by logistic regression.
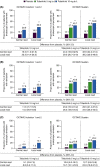
Results: Moderate-to-substantial agreement was observed between central and local reads at screening (77.1% agreement; kappa 0.62 [95% confidence interval 0.59-0.66]), OCTAVE Induction 1&2 week (Wk) 8 (63.8%; 0.62 [0.59-0.66]), OCTAVE Sustain Wk 52 (55.6%; 0.56 [0.50-0.62]) and for induction non-responders at OCTAVE Open month 2 (59.9%; 0.54 [0.48-0.60]). Where disagreements occurred, local reads were systematically lower than central reads at OCTAVE Induction 1&2 Wk 8, OCTAVE Sustain Wk 52 and OCTAVE Open month 2 (Bowker's P < 0.0001); this difference was not observed at screening (P = 0.0852). Using multivariable logistic regression, geographical region, C-reactive protein (Wk 8), partial Mayo score (Wk 8) and prior tumour necrosis factor antagonist failure were associated with disparity at OCTAVE Induction 1&2 Wk 8 (P < 0.05). In OCTAVE Induction 1&2 and OCTAVE Sustain, significantly higher proportions of patients endoscopic improvement, remission and endoscopic remission with tofacitinib vs placebo, using either central or local reads.
Conclusion: Moderate-to-substantial agreement was observed between central and local endoscopic reads. Where disagreements occurred, local reads were systematically lower than central reads at most timepoints, suggesting potential bias. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01465763, NCT01458951, NCT01458574, NCT01470612.
Keywords: endoscopy; inflammatory bowel disease; symptom score or index; ulcerative colitis.
© 2021 Pfizer Inc. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Comment in
-
Editorial: don't forget basic performance measures in the endoscopic assessment of ulcerative colitis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Jan;55(1):129-130. doi: 10.1111/apt.16679. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34907554 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vuitton L, Peyrin‐Biroulet L, Colombel JF, et al. Defining endoscopic response and remission in ulcerative colitis clinical trials: an international consensus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45:801‐813. - PubMed
-
- D’Haens G, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. A review of activity indices and efficacy end points for clinical trials of medical therapy in adults with ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:763‐786. - PubMed
-
- Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, D'Haens G, et al. The role of centralized reading of endoscopy in a randomized controlled trial of mesalamine for ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:149‐157. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Ulcerative colitis: clinical trial endpoints. Guidance for industry. 2016. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/Guidances/UCM515143.pdf. Accessed July 8, 2021.
-
- European Medicines Agency Guideline on the development of new medicinal products for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. 2018. https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/scientific‐guideline/guideline‐devel... Accessed July 8, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
