Cargo-specific recruitment in clathrin- and dynamin-independent endocytosis
- PMID: 34616024
- PMCID: PMC7617174
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-021-00767-x
Cargo-specific recruitment in clathrin- and dynamin-independent endocytosis
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Cargo-specific recruitment in clathrin- and dynamin-independent endocytosis.Nat Cell Biol. 2022 Sep;24(9):1445. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00952-6. Nat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 36038735 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
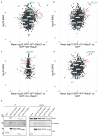
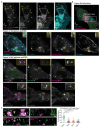
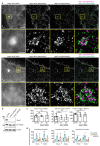
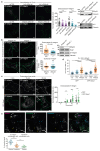
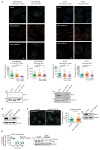
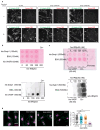
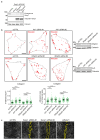
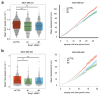
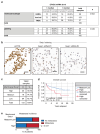
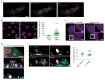
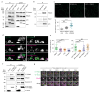
Spatially controlled, cargo-specific endocytosis is essential for development, tissue homeostasis and cancer invasion. Unlike cargo-specific clathrin-mediated endocytosis, the clathrin- and dynamin-independent endocytic pathway (CLIC-GEEC, CG pathway) is considered a bulk internalization route for the fluid phase, glycosylated membrane proteins and lipids. While the core molecular players of CG-endocytosis have been recently defined, evidence of cargo-specific adaptors or selective uptake of proteins for the pathway are lacking. Here we identify the actin-binding protein Swiprosin-1 (Swip1, EFHD2) as a cargo-specific adaptor for CG-endocytosis. Swip1 couples active Rab21-associated integrins with key components of the CG-endocytic machinery-Arf1, IRSp53 and actin-and is critical for integrin endocytosis. Through this function, Swip1 supports integrin-dependent cancer-cell migration and invasion, and is a negative prognostic marker in breast cancer. Our results demonstrate a previously unknown cargo selectivity for the CG pathway and a role for specific adaptors in recruitment into this endocytic route.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Comment in
-
CLICing on endocytic cargoes for cancer invasion.Nat Cell Biol. 2021 Oct;23(10):1052-1053. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00763-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34616023 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

