Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles
- PMID: 34616401
- PMCID: PMC8488215
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.733064
Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles as Antibiotic Delivery Vehicles
Abstract
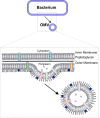
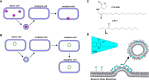
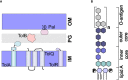
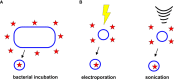
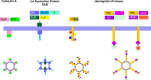
Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are nanometer-scale, spherical vehicles released by Gram-negative bacteria into their surroundings throughout growth. These OMVs have been demonstrated to play key roles in pathogenesis by delivering certain biomolecules to host cells, including toxins and other virulence factors. In addition, this biomolecular delivery function enables OMVs to facilitate intra-bacterial communication processes, such as quorum sensing and horizontal gene transfer. The unique ability of OMVs to deliver large biomolecules across the complex Gram-negative cell envelope has inspired the use of OMVs as antibiotic delivery vehicles to overcome transport limitations. In this review, we describe the advantages, applications, and biotechnological challenges of using OMVs as antibiotic delivery vehicles, studying both natural and engineered antibiotic applications of OMVs. We argue that OMVs hold great promise as antibiotic delivery vehicles, an urgently needed application to combat the growing threat of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Gram-negative bacteria; antibiotic resistance; antibiotics; drug delivery; outer membrane vesicles.
Copyright © 2021 Collins and Brown.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- U.S.Department of Health and Human Services Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States. Atlanta, GA:U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; (2019). doi: 10.15620/cdc:82532 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

