Exosomal hsa-miR-21-5p is a biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis
- PMID: 34616615
- PMCID: PMC8451442
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12147
Exosomal hsa-miR-21-5p is a biomarker for breast cancer diagnosis
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer (BC) is characterized by concealed onset, delayed diagnosis, and high fatality rates making it particularly dangerous to patients' health. The purpose of this study was to use comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification to find a new biomarker for BC diagnosis.
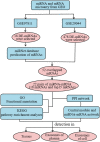
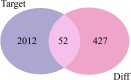
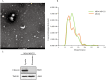
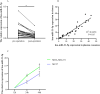
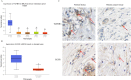
Methods: We comprehensively analyzed microRNA (miRNA) and mRNA expression profiles from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and screened out differentially-expressed (DE) miRNAs and mRNAs. We used the miRNet website to predict potential DE-miRNA target genes. Using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID), we performed Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses on overlapping potential target genes and DE-mRNAs. The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was then established. The miRNA-mRNA regulatory network was constructed using Cytoscape and the analysis results were visualized. We verified the expression of the most up-regulated DE-miRNA using reverse transcription and a quantitative polymerase chain reaction in BC tissue. The diagnostic value of the most up-regulated DE-miRNA was further explored across three levels: plasma-derived exosomes, cells, and cell exosomes.
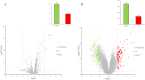
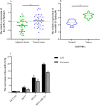
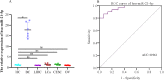
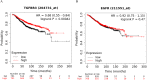
Results: Our comprehensive bioinformatics analysis and experimental results showed that hsa-miR-21-5p was significantly up-regulated in BC tissue, cells, and exosomes. Our results also revealed that tumor-derived hsa-miR-21-5p could be packaged in exosomes and released into peripheral blood. Additionally, when evaluating the diagnostic value of plasma exosomal hsa-miR-21-5p, we found that it was significantly up-regulated in BC patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis also confirmed that hsa-miR-21-5p could effectively distinguish healthy people from BC patients. The sensitivity and specificity were 86.7% and 93.3%, respectively.
Conclusion: This study's results showed that plasma exosomal hsa-miR-21-5p could be used as a biomarker for BC diagnosis.
Keywords: Bioinformatics; Biomarker; Breast cancer; Diagnosis; Exosome; microRNA.
©2021 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Bevers TB, Helvie M, Bonaccio E, Calhoun KE, Daly MB, Farrar WB, Garber JE, Gray R, Greenberg CC, Greenup R, Hansen NM, Harris RE, Heerdt AS, Helsten T, Hodgkiss L, Hoyt TL, Huff JG, Jacobs L, Lehman CD, Monsees B, Niell BL, Parker CC, Pearlman M, Philpotts L, Shepardson LB, Smith ML, Stein M, Tumyan L, Williams C, Bergman MA, Kumar R. Breast cancer screening and diagnosis, version 3.2018, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. 2018;16:1362–1389. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2018.0083. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Chen R, Kemper S, Charrier A, Brigstock DR. Suppression of fibrogenic signaling in hepatic stellate cells by Twist1-dependent microRNA-214 expression: role of exosomes in horizontal transfer of Twist1. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2015;309:G491–499. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00140.2015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

