SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test in comparison to RT-PCR targeting different genes: A real-life evaluation among unselected patients in a regional hospital of Italy
- PMID: 34617606
- PMCID: PMC8661633
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.27378
SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test in comparison to RT-PCR targeting different genes: A real-life evaluation among unselected patients in a regional hospital of Italy
Abstract
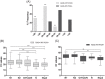
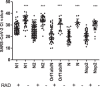
We assessed the performance of the Panbio rapid antigen detection (RAD) test for the detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and we compared it with the routine reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)-based molecular test in a population of 4167 unselected patients admitted to IRCCS Sacro Cuore Don Calabria Hospital. Analysis stratified by cycling threshold (Ct ) value of SARS-CoV-2 gene targets indicated that antigen (Ag)-positive Ct values were significantly lower compared to Ag-negative values (p < 0.0001). Overall, we found discordance in 140, tested negative by RAD and positive by RT-PCR, and in 4 resulted positive by RAD and negative by RT-PCR. RAD test achieved a sensitivity and specificity of 66.82% and 99.89%, respectively. The positive predictive value was shown to be 97.87% while the negative predictive value was shown to be 97.62%. In our context, the RAD test showed a reliable diagnostic response in subjects that displayed high Ct values, corresponding to high viral load, while low ability was displayed to identify positive cases with medium-low Ct values, thus presenting low viral load and where confirmatory RT-PCR was needed. Our finding supports the use of the RAD test in real-life settings where a high volume of swabs is being processed but with caution when interpreting a positive test result in a low prevalence setting.
Keywords: Panbio™ COVID-19; RAD; RT-PCR; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Medical Virology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- ECDC. Options for the use of rapid antigen tests for COVID‐19 in the EU/EEA and the UK; 2020
-
- World Health Organization. Antigen‐detection in the diagnosis of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection using rapid immunoassays interim guidance; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

