Evaluation of Genome Sequences of the Bacteriophages JeTaime and Luna22
- PMID: 34617782
- PMCID: PMC8496362
- DOI: 10.1128/MRA.00746-21
Evaluation of Genome Sequences of the Bacteriophages JeTaime and Luna22
Abstract
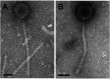
The mycobacteriophages JeTaime (E cluster) and Luna22 (Q cluster) were isolated from soil in Providence, Rhode Island, and Charleston, South Carolina, respectively, using a Mycobacterium smegmatis mc2 155 host. The genome of JeTaime is 75,099 bp (142 predicted genes), and that of Luna22 is 53,730 bp (87 predicted genes). Both phages exhibit Siphoviridae morphology.
Figures
References
-
- Jordan TC, Burnett SH, Carson S, Caruso SM, Clase K, DeJong RJ, Dennehy JJ, Denver DR, Dunbar D, Elgin SCR, Findley AM, Gissendanner CR, Golebiewska UP, Guild N, Hartzog GA, Grillo WH, Hollowell GP, Hughes LE, Johnson A, King RA, Lewis LO, Li W, Rosenzweig F, Rubin MR, Saha MS, Sandoz J, Shaffer CD, Taylor B, Temple L, Vazquez E, Ware VC, Barker LP, Bradley KW, Jacobs-Sera D, Pope WH, Russell DA, Cresawn SG, Lopatto D, Bailey CP, Hatfull GF. 2014. A broadly implementable research course in phage discovery and genomics for first-year undergraduate students. mBio 5:e01051-13. doi:10.1128/mBio.01051-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poxleitner M, Pope W, Jacobs-Sera D, Sivanathan V, Hatfull G. 2018. Phage discovery guide. Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Chevy Chase, MD. http://seaphagesphagediscoveryguide.helpdocsonline.com/home.
-
- Margulies M, Egholm M, Altman WE, Attiya S, Bader JS, Bemben LA, Berka J, Braverman MS, Chen Y-J, Chen Z, Dewell SB, Du L, Fierro JM, Gomes XV, Godwin BC, He W, Helgesen S, Ho CH, Irzyk GP, Jando SC, Alenquer MLI, Jarvie TP, Jirage KB, Kim J-B, Knight JR, Lanza JR, Leamon JH, Lefkowitz SM, Lei M, Li J, Lohman KL, Lu H, Makhijani VB, McDade KE, McKenna MP, Myers EW, Nickerson E, Nobile JR, Plant R, Puc BP, Ronan MT, Roth GT, Sarkis GJ, Simons JF, Simpson JW, Srinivasan M, Tartaro KR, Tomasz A, Vogt KA, Volkmer GA, Wang SH, Wang Y, Weiner MP, Yu P, Begley RF, Rothberg JM. 2005. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 437:376–380. doi:10.1038/nature03959. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
