Capillary Venous Malformation With Secondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of Temporal Bone
- PMID: 34617902
- PMCID: PMC8975380
- DOI: 10.5152/iao.2021.8124
Capillary Venous Malformation With Secondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of Temporal Bone
Abstract
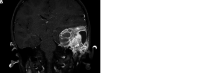
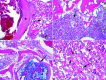
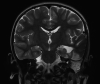
Aneurysmal bone cysts (ABCs) arising from vascular malformation are extremely rare, and none have been reported in the literature in English till now. We report a very rare case of secondary ABC of left temporal bone in a 5-year-old Caucasian boy who presented with a left sudden facial palsy associated with a painless non-tender mass of the left temporo-parietal region. The computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) features were suggestive of ABC secondary to a capillary venous malformation, with concurrent involvement of the squamous, mastoid, and petrous portions of the temporal bone. Surgical resection was performed. On follow-up, the patient was found to be doing well.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kim BJ, Lee EJ, Chang HW, et al. Aneurysmal bone cyst in the temporal bone and complete resection with preoperative embolization. A case report. Interv Neuroradiol. 2014;20(5):609–613.. 10.15274/INR-2014-10051 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kletke SN, Popovic S, Algirdur A. Aneurysmal bone cyst of the temporal bone presenting with headache and partial facial palsy. J Neurol Surg Rep. 2015;76: e18–e22.. 10.1055/s-0034-1390020 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
