Elicitation of broadly protective sarbecovirus immunity by receptor-binding domain nanoparticle vaccines
- PMID: 34619077
- PMCID: PMC8440233
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.015
Elicitation of broadly protective sarbecovirus immunity by receptor-binding domain nanoparticle vaccines
Abstract
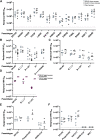
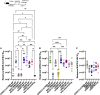
Understanding vaccine-elicited protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and other sarbecoviruses is key for guiding public health policies. We show that a clinical stage multivalent SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain nanoparticle (RBD-NP) vaccine protects mice from SARS-CoV-2 challenge after a single immunization, indicating a potential dose-sparing strategy. We benchmarked serum neutralizing activity elicited by RBD-NPs in non-human primates against a lead prefusion-stabilized SARS-CoV-2 spike (HexaPro) using a panel of circulating mutants. Polyclonal antibodies elicited by both vaccines are similarly resilient to many RBD residue substitutions tested, although mutations at and surrounding position 484 have negative consequences for neutralization. Mosaic and cocktail nanoparticle immunogens displaying multiple sarbecovirus RBDs elicit broad neutralizing activity in mice and protect mice against SARS-CoV challenge even in the absence of SARS-CoV RBD in the vaccine. This study provides proof of principle that multivalent sarbecovirus RBD-NPs induce heterotypic protection and motivates advancing such broadly protective sarbecovirus vaccines to the clinic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; mosaic nanoparticle; receptor-binding domain; sarbecovirus; self-assembling nanoparticle; spike glycoprotein; vaccine design.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A.C.W., N.P.K., and D.V. are named as inventors on patent applications filed by the University of Washington based on the studies presented in this paper. N.P.K. is a co-founder, shareholder, paid consultant, and chair of the scientific advisory board of Icosavax, Inc. and has received an unrelated sponsored research agreement from Pfizer. D.C. is an employee of Vir Biotechnology and may hold shares in Vir Biotechnology. D.V. is a consultant for and has received an unrelated sponsored research agreement from Vir Biotechnology, Inc. R.R., D.T.O., and R.V.D.M. are employees of GlaxoSmithKline. C.-L.H. and J.S.M. are inventors on US patent application no. 63/032,502, “Engineered Coronavirus Spike (S) Protein and Methods of Use Thereof”. R.S.B. has collaborative research agreements with Takeda, Pfizer, Eli Lily, Gilead, Ridgeback Biosciences, and VaxArt, unrelated to the current research. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Elicitation of broadly protective sarbecovirus immunity by receptor-binding domain nanoparticle vaccines.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2021 Mar 16:2021.03.15.435528. doi: 10.1101/2021.03.15.435528. bioRxiv. 2021. Update in: Cell. 2021 Oct 14;184(21):5432-5447.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.09.015. PMID: 33758839 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Abu Jabal K., Ben-Amram H., Beiruti K., Batheesh Y., Sussan C., Zarka S., Edelstein M. Impact of age, ethnicity, sex and prior infection status on immunogenicity following a single dose of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: real-world evidence from healthcare workers, Israel, December 2020 to January 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021;26:2100096. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arunachalam P.S., Walls A.C., Golden N., Atyeo C., Fischinger S., Li C., Aye P., Navarro M.J., Lai L., Edara V.V., et al. Adjuvanting a subunit COVID-19 vaccine to induce protective immunity. Nature. 2021;594:253–258. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

