Immunological responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 34619100
- PMCID: PMC8489877
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02096-1
Immunological responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in kidney transplant recipients
Conflict of interest statement
PK and MW have received support to use the T-SPOT Discovery SARS-CoV-2 by Oxford Immunotec. MP, TT, and CLC contributed equally. Members of the Imperial Renal COVID-19 vaccine study group are listed in the appendix (pp 25–26). All other authors declare no competing interests.
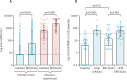
Figures
Comment on
-
Comparative systematic review and meta-analysis of reactogenicity, immunogenicity and efficacy of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.NPJ Vaccines. 2021 May 13;6(1):74. doi: 10.1038/s41541-021-00336-1. NPJ Vaccines. 2021. PMID: 33986272 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

