Coordinated regulation of the ribosome and proteasome by PRMT1 in the maintenance of neural stemness in cancer cells and neural stem cells
- PMID: 34619150
- PMCID: PMC8546425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101275
Coordinated regulation of the ribosome and proteasome by PRMT1 in the maintenance of neural stemness in cancer cells and neural stem cells
Abstract
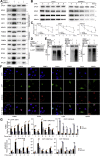
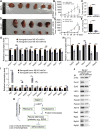
Previous studies suggested that cancer cells resemble neural stem/progenitor cells in regulatory network, tumorigenicity, and differentiation potential, and that neural stemness might represent the ground or basal state of differentiation and tumorigenicity. The neural ground state is reflected in the upregulation and enrichment of basic cell machineries and developmental programs, such as cell cycle, ribosomes, proteasomes, and epigenetic factors, in cancers and in embryonic neural or neural stem cells. However, how these machineries are concertedly regulated is unclear. Here, we show that loss of neural stemness in cancer or neural stem cells via muscle-like differentiation or neuronal differentiation, respectively, caused downregulation of ribosome and proteasome components and major epigenetic factors, including PRMT1, EZH2, and LSD1. Furthermore, inhibition of PRMT1, an oncoprotein that is enriched in neural cells during embryogenesis, caused neuronal-like differentiation, downregulation of a similar set of proteins downregulated by differentiation, and alteration of subcellular distribution of ribosome and proteasome components. By contrast, PRMT1 overexpression led to an upregulation of these proteins. PRMT1 interacted with these components and protected them from degradation via recruitment of the deubiquitinase USP7, also known to promote cancer and enriched in embryonic neural cells, thereby maintaining a high level of epigenetic factors that maintain neural stemness, such as EZH2 and LSD1. Taken together, our data indicate that PRMT1 inhibition resulted in repression of cell tumorigenicity. We conclude that PRMT1 coordinates ribosome and proteasome activity to match the needs for high production and homeostasis of proteins that maintain stemness in cancer and neural stem cells.
Keywords: PRMT1; USP7; cancer cell; cell differentiation; deubiquitination; neural stem cell (NSC); neural stemness; proteasome; ribosome; tumorigenicity.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neural stemness unifies cell tumorigenicity and pluripotent differentiation potential.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jul;298(7):102106. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102106. Epub 2022 Jun 4. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35671824 Free PMC article.
-
PRMT1 regulates the tumour-initiating properties of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through histone H4 arginine methylation coupled with transcriptional activation.Cell Death Dis. 2019 May 1;10(5):359. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1595-0. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31043582 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) in brain development and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021 Jan;1865(1):129776. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129776. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2021. PMID: 33127433 Review.
-
The dual function of PRMT1 in modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence in breast cancer cells through regulation of ZEB1.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 27;6:19874. doi: 10.1038/srep19874. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26813495 Free PMC article.
-
Neural is Fundamental: Neural Stemness as the Ground State of Cell Tumorigenicity and Differentiation Potential.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022 Jan;18(1):37-55. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10275-y. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022. PMID: 34714532 Review.
Cited by
-
PRMT1 promotes radiotherapy resistance in glioma stem cells by inhibiting ferroptosis.Jpn J Radiol. 2025 Jan;43(1):129-137. doi: 10.1007/s11604-024-01651-y. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Jpn J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39254902
-
Critical Roles of Protein Arginine Methylation in the Central Nervous System.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):6060-6091. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03465-x. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37415067 Review.
-
Regulation of neural stem cell proliferation and survival by protein arginine methyltransferase 1.Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 10;16:948517. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.948517. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36440275 Free PMC article.
-
Neural induction drives body axis formation during embryogenesis, but a neural induction-like process drives tumorigenesis in postnatal animals.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 May 9;11:1092667. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1092667. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37228646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferases from Regulatory Function to Clinical Implication in Central Nervous System.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 May 14;45(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01546-0. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40366461 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

