Defining biological and biophysical properties of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material in wastewater
- PMID: 34619200
- PMCID: PMC8490134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150786
Defining biological and biophysical properties of SARS-CoV-2 genetic material in wastewater
Abstract
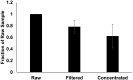
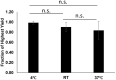
SARS-CoV-2 genetic material has been detected in raw wastewater around the world throughout the COVID-19 pandemic and has served as a useful tool for monitoring community levels of SARS-CoV-2 infections. SARS-CoV-2 genetic material is highly detectable in a patient's feces and the household wastewater for several days before and after a positive COVID-19 qPCR test from throat or sputum samples. Here, we characterize genetic material collected from raw wastewater samples and determine recovery efficiency during a concentration process. We find that pasteurization of raw wastewater samples did not reduce SARS-CoV-2 signal if RNA is extracted immediately after pasteurization. On the contrary, we find that signal decreased by approximately half when RNA was extracted 24-36 h post-pasteurization and ~90% when freeze-thawed prior to concentration. As a matrix control, we use an engineered enveloped RNA virus. Surprisingly, after concentration, the recovery of SARS-CoV-2 signal is consistently higher than the recovery of the control virus leading us to question the nature of the SARS-CoV-2 genetic material detected in wastewater. We see no significant difference in signal after different 24-hour temperature changes; however, treatment with detergent decreases signal ~100-fold. Furthermore, the density of the samples is comparable to enveloped retrovirus particles, yet, interestingly, when raw wastewater samples were used to inoculate cells, no cytopathic effects were seen indicating that wastewater samples do not contain infectious SARS-CoV-2. Together, this suggests that wastewater contains fully intact enveloped particles.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Pasteurization; Sewage; Surveillance; Wastewater.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

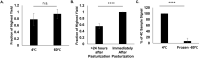




References
-
- Bivins A., et al. Wastewater-based epidemiology: global collaborative to maximize contributions in the fight against COVID-19. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020;54(13):7754–7757. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

