The European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU): Human biomonitoring guidance values (HBM-GVs) for the aprotic solvents N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) and N-ethyl-2-pyrrolidone (NEP)
- PMID: 34619432
- PMCID: PMC8573589
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2021.113856
The European Human Biomonitoring Initiative (HBM4EU): Human biomonitoring guidance values (HBM-GVs) for the aprotic solvents N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) and N-ethyl-2-pyrrolidone (NEP)
Abstract
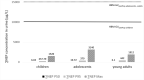
Toxicologically and/or epidemiologically derived guidance values referring to the internal exposure of humans are a prerequisite for an easy to use health-based interpretation of human biomonitoring (HBM) results. The European Joint Programme HBM4EU derives such values, named human biomonitoring guidance values (HBM-GVs), for priority substances which could be of regulatory relevance for policy makers and have been identified by experts of the participating countries, ministries, agencies and stakeholders at EU and national level. NMP and NEP are such substances for which unresolved policy relevant issues should be clarified by targeted research. Since widespread exposure of the general population in Germany to NMP and NEP was shown for the age groups 3-17 years and 20-29 years, further investigations on exposure to NMP and NEP in other European countries are warranted. The HBM-GVs derived for both solvents focus on developmental toxicity as decisive endpoint. They amount for the sum of the two specific urinary NMP metabolites 5-HNMP and 2-HMSI and likewise of the two specific urinary NEP metabolites 5-HNEP and 2-HESI to 10 mg/L for children and 15 mg/L for adolescents/adults. The values were determined following a consultation process on the value proposals within HBM4EU. A health-based risk assessment was performed using the newly derived HBM-GVGenPop and exposure data from two recent studies from Germany. The risk assessment revealed that even when considering the combined exposure to both substances by applying the Hazard Index approach, the measured concentrations are below the HBM-GVGenPop in all cases investigated (i.e., children, adolescents and young adults).
Keywords: Aprotic solvents; HBM4EU; Human biomonitoring guidance value (HBM-GV); N-ethyl-2-pyrrolidone (NEP); N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP); Risk assessment.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier GmbH.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Åkesson B., Jönsson B.A.g. Major metabolic pathway for N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone in humans. Drug Metabol. Dispos. 1997;25:267–269. - PubMed
-
- Akrill P., Cocker J., Dixon S. Dermal exposure to aqueous solutions of N-methyl pyrrolidone. Toxicol. Lett. 2002;134:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Anderson H.A., Wolff M.S. Environmental contaminants in human milk. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2000;10:755–760. - PubMed
-
- Angerer J., Aylward L.L., Hays S.M., Heinzow B., Wilhelm M. Human biomonitoring assessment values: approaches and data requirements. Int. J. Hyg Environ. Health. 2011;214:348–360. - PubMed
-
- ANSES . 2014. Reference Document for the Derivation and the Measurement of Exposure Limit Values for Chemical Agents in the Workplace (OELs), French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety (ANSES)https://www.anses.fr/en/system/files/VLEP2009sa0339RaEN.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

