Identification of immunization-related new prognostic biomarkers for papillary renal cell carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 34620162
- PMCID: PMC8499437
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-021-01092-w
Identification of immunization-related new prognostic biomarkers for papillary renal cell carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: Despite papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) being the second most common type of kidney cancer, the underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear. Targeted therapies in the past have not been successful because of the lack of a clear understanding of the molecular mechanism. Hence, exploring the underlying mechanisms and seeking novel biomarkers for pursuing a precise prognostic biomarker and appropriate therapies are critical.
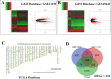
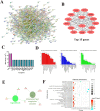
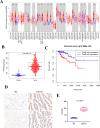
Material and methods: In our research, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened from the TCGA and GEO databases, and a total of 149 upregulated and 285 downregulated genes were sorted. This was followed by construction of functional enrichment and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, and then the top 15 DEGs were selected for further analysis. The P4HB gene was chosen as our target gene by repetitively validating multiple datasets, and higher levels of P4HB expression predicted lower overall survival (OS) in patients with pRCC.
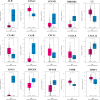
Results: We found that P4HB not only connects with immune cell infiltration and co-expression with PD-1, PD-L2, and CTLA-4, but also has a strong connection with the newly discovered hot gene, TOX.
Conclusion: We speculate that P4HB is a novel gene involved in the progression of pRCC through immunomodulation.
Keywords: Biological markers; Carcinoma; Computational biology; Immunotherapy; Prolyl hydroxylases; Renal cell.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Screening and identification of key biomarkers of papillary renal cell carcinoma by bioinformatic analysis.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 6;16(8):e0254868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254868. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34358255 Free PMC article.
-
The underlying molecular mechanism and potential drugs for treatment in papillary renal cell carcinoma: A study based on TCGA and Cmap datasets.Oncol Rep. 2019 Apr;41(4):2089-2102. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7014. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 30816528 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of CXCL13 as a potential biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via comprehensive bioinformatics analysis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Oct;118:109264. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109264. Epub 2019 Aug 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31390578
-
Integrated Phenotypic/Genotypic Analysis of Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes: Identification of Prognostic Markers, Cancer-related Pathways, and Implications for Therapy.Eur Urol Focus. 2018 Sep;4(5):740-748. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2016.09.002. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Eur Urol Focus. 2018. PMID: 28753789
-
Diagnostic and prognostic tissuemarkers in clear cell and papillary renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2010;7(6):261-8. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2010-0195. Cancer Biomark. 2010. PMID: 21694464 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of P4HB as a novel autophagy-related biomarker in diabetic nephropathy.Front Genet. 2022 Sep 26;13:965816. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.965816. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36226178 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit beta (P4HB) could serve as a prognostic and radiosensitivity biomarker for prostate cancer patients.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Jul 22;28(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01215-2. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37480146 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Subunit Beta (P4HB) in Cancer: New Roads to Travel.Aging Dis. 2023 Nov 26;15(6):2369-2380. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.1126. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 38029391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity-Dependent Association of the rs10454142 PPP1R21 with Breast Cancer.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 8;12(4):818. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040818. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

