COVID-19-related research in Africa: a cross-sectional review of the International Clinical Trial Registration Platform (ICTRP)
- PMID: 34620207
- PMCID: PMC8496615
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-021-05621-x
COVID-19-related research in Africa: a cross-sectional review of the International Clinical Trial Registration Platform (ICTRP)
Abstract
Objective: The declaration of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), a pandemic in early 2020, has seen an upsurge in research globally to fill gaps in the epidemiology of the SARS-CoV-2 virus impact on health care and clinical management, as well as possible prevention and treatment modalities. Published literature on the different types of COVID-19 research conducted globally is varied and is particularly limited in Africa. This study sets out to describe the COVID-19-related research registered and conducted on the African continent.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of all COVID-19-related studies available in the WHO's International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) repository. We extracted studies registered from March 1, 2020, to July 15, 2021. A descriptive analysis of the extracted data was performed, and the findings were presented.
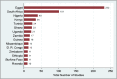
Results: At extraction, a total of 12,533 COVID-19-related studies were listed on the ICTRP portal. We included 9803 studies, after excluding 2060 duplicate records and 686 records without a site/country. While 9347 studies (96%) were conducted outside of Africa, only 456 studies (4%) were conducted in the African continent, of which 270 (59.2%) were interventional studies, and 184 (40.4%) were observational studies. About 80% of the studies were conducted in Egypt and South Africa, and most of these involved testing of drugs and biologicals.
Conclusion: The African continent hosts considerably fewer COVID-19-related research compared to other parts of the world. This may have implications on scientific evidence available for implementing COVID-19 control efforts. There is, therefore, a need for local funding and ownership of research projects and north-south collaboration in research.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang W, Ou C, He J, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, du B, Li LJ, Zeng G, Yuen KY, Chen RC, Tang CL, Wang T, Chen PY, Xiang J, Li SY, Wang JL, Liang ZJ, Peng YX, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu YH, Peng P, Wang JM, Liu JY, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng ZJ, Qiu SQ, Luo J, Ye CJ, Zhu SY, Zhong NS, China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19 Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708–1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Juul S, Nielsen EE, Feinberg J, Siddiqui F, Jørgensen CK, Barot E, Nielsen N, Bentzer P, Veroniki AA, Thabane L, Bu F, Klingenberg S, Gluud C, Jakobsen JC. Interventions for treatment of COVID-19: a living systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses (The LIVING Project) PLoS Med. 2020;17(9):1–25. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003293. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edem B, Onwuchekwa C, Wariri O, Nkereuwem E, Nkereuwem OO, Williams V. Trends in clinical trial registration in sub-Saharan Africa between 2010 and 2020: a cross-sectional review of three clinical trial registries. Trials. 2021;22(1):1–11. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-021-05423-1 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

