Clinical evolution, genetic landscape and trajectories of clonal hematopoiesis in SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes
- PMID: 34621053
- PMCID: PMC9330547
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-021-01511-6
Clinical evolution, genetic landscape and trajectories of clonal hematopoiesis in SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Clinical evolution, genetic landscape and trajectories of clonal hematopoiesis in SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes.Nat Med. 2021 Dec;27(12):2248. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01632-y. Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 34799732 No abstract available.
Abstract
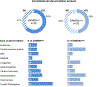
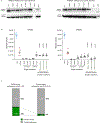
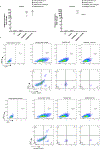
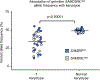
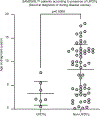
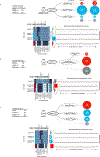
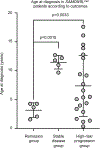
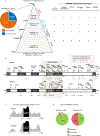
Germline SAMD9 and SAMD9L mutations (SAMD9/9Lmut) predispose to myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) with propensity for somatic rescue. In this study, we investigated a clinically annotated pediatric MDS cohort (n = 669) to define the prevalence, genetic landscape, phenotype, therapy outcome and clonal architecture of SAMD9/9L syndromes. In consecutively diagnosed MDS, germline SAMD9/9Lmut accounted for 8% and were mutually exclusive with GATA2 mutations present in 7% of the cohort. Among SAMD9/9Lmut cases, refractory cytopenia was the most prevalent MDS subtype (90%); acquired monosomy 7 was present in 38%; constitutional abnormalities were noted in 57%; and immune dysfunction was present in 28%. The clinical outcome was independent of germline mutations. In total, 67 patients had 58 distinct germline SAMD9/9Lmut clustering to protein middle regions. Despite inconclusive in silico prediction, 94% of SAMD9/9Lmut suppressed HEK293 cell growth, and mutations expressed in CD34+ cells induced overt cell death. Furthermore, we found that 61% of SAMD9/9Lmut patients underwent somatic genetic rescue (SGR) resulting in clonal hematopoiesis, of which 95% was maladaptive (monosomy 7 ± cancer mutations), and 51% had adaptive nature (revertant UPD7q, somatic SAMD9/9Lmut). Finally, bone marrow single-cell DNA sequencing revealed multiple competing SGR events in individual patients. Our findings demonstrate that SGR is common in SAMD9/9Lmut MDS and exemplify the exceptional plasticity of hematopoiesis in children.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures







Comment in
-
Pediatric Pancytopenia and Monosomy 7: A Case Report of SAMD9L-Associated Disease.J Clin Immunol. 2024 Jan 17;44(2):43. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01650-0. J Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38231353 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nagamachi A, et al. Haploinsufficiency of SAMD9L, an endosome fusion facilitator, causes myeloid malignancies in mice mimicking human diseases with monosomy 7. Cancer Cell 24, 305–317 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

