A fully deep learning model for the automatic identification of cephalometric landmarks
- PMID: 34621657
- PMCID: PMC8479429
- DOI: 10.5624/isd.20210077
A fully deep learning model for the automatic identification of cephalometric landmarks
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to propose a fully automatic landmark identification model based on a deep learning algorithm using real clinical data and to verify its accuracy considering inter-examiner variability.
Materials and methods: In total, 950 lateral cephalometric images from Yonsei Dental Hospital were used. Two calibrated examiners manually identified the 13 most important landmarks to set as references. The proposed deep learning model has a 2-step structure-a region of interest machine and a detection machine-each consisting of 8 convolution layers, 5 pooling layers, and 2 fully connected layers. The distance errors of detection between 2 examiners were used as a clinically acceptable range for performance evaluation.
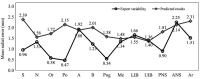
Results: The 13 landmarks were automatically detected using the proposed model. Inter-examiner agreement for all landmarks indicated excellent reliability based on the 95% confidence interval. The average clinically acceptable range for all 13 landmarks was 1.24 mm. The mean radial error between the reference values assigned by 1 expert and the proposed model was 1.84 mm, exhibiting a successful detection rate of 36.1%. The A-point, the incisal tip of the maxillary and mandibular incisors, and ANS showed lower mean radial error than the calibrated expert variability.
Conclusion: This experiment demonstrated that the proposed deep learning model can perform fully automatic identification of cephalometric landmarks and achieve better results than examiners for some landmarks. It is meaningful to consider between-examiner variability for clinical applicability when evaluating the performance of deep learning methods in cephalometric landmark identification.
Keywords: Anatomic Landmarks; Artificial Intelligence; Deep Learning; Dental Digital Radiography; Neural Network Models.
Copyright © 2021 by Korean Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automatic identification of posteroanterior cephalometric landmarks using a novel deep learning algorithm: a comparative study with human experts.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 19;13(1):15506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42870-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37726392 Free PMC article.
-
Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: Part 2-Might it be better than human?.Angle Orthod. 2020 Jan;90(1):69-76. doi: 10.2319/022019-129.1. Epub 2019 Jul 22. Angle Orthod. 2020. PMID: 31335162 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of automated identification of lateral cephalometric landmarks using cascade convolutional neural networks on lateral cephalograms from nationwide multi-centres.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2021 Dec;24 Suppl 2:59-67. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12493. Epub 2021 Jun 27. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2021. PMID: 33973341
-
Evaluation of deep learning and convolutional neural network algorithms accuracy for detecting and predicting anatomical landmarks on 2D lateral cephalometric images: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Saudi Dent J. 2023 Jul;35(5):487-497. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 May 23. Saudi Dent J. 2023. PMID: 37520606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, Application, and Performance of Artificial Intelligence in Cephalometric Landmark Identification and Diagnosis: A Systematic Review.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 5;10(12):2454. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10122454. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Using AI in Optimizing Oral and Dental Diagnoses-A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Dec 13;14(24):2804. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242804. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the quality of different commercial providers using artificial intelligence for automated cephalometric analysis compared to human orthodontic experts.J Orofac Orthop. 2025 May;86(3):145-160. doi: 10.1007/s00056-023-00491-1. Epub 2023 Aug 29. J Orofac Orthop. 2025. PMID: 37642657 Free PMC article.
-
Forensic Gender Determination by Using Mandibular Morphometric Indices an Iranian Population: A Panoramic Radiographic Cross-Sectional Study.J Imaging. 2023 Feb 11;9(2):40. doi: 10.3390/jimaging9020040. J Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36826959 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Automated Cephalometric Landmark Identification: A Meta-Analysis Previewed by a Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Jun 25;15(6):e40934. doi: 10.7759/cureus.40934. eCollection 2023 Jun. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37496553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning with convolution neural network detecting mesiodens on panoramic radiographs: comparing four models.Odontology. 2025 Jan;113(1):448-455. doi: 10.1007/s10266-024-00980-8. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Odontology. 2025. PMID: 39017730
References
-
- Broadbent BH. A new x-ray technique and its application to orthodontia. Angle Orthod. 1931;1:45–66.
-
- Yang J, Ling X, Lu Y, Wei M, Ding G. Cephalometric image analysis and measurement for orthognathic surgery. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2001;39:279–284. - PubMed
-
- Houston WJ. The analysis of errors in orthodontic measurements. Am J Orthod. 1983;83:382–390. - PubMed

