Reward-Based Decision-Making Engages Distinct Modes of Cross-Frequency Coupling
- PMID: 34622271
- PMCID: PMC9113280
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhab336
Reward-Based Decision-Making Engages Distinct Modes of Cross-Frequency Coupling
Abstract
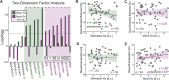
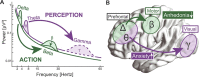
Prefrontal cortex exerts control over sensory and motor systems via cross-frequency coupling. However, it is unknown whether these signals play a role in reward-based decision-making and whether such dynamic network configuration is altered in a major depressive episode. We recruited men and women with and without depression to perform a streamlined version of the Expenditure of Effort for Reward Task during recording of electroencephalography. Goal-directed behavior was quantified as willingness to exert physical effort to obtain reward, and reward-evaluation was the degree to which the decision to exert effort was modulated by incentive level. We found that the amplitude of frontal-midline theta oscillations was greatest in participants with the greatest reward-evaluation. Furthermore, coupling between frontal theta phase and parieto-occipital gamma amplitude was positively correlated with reward-evaluation. In addition, goal-directed behavior was positively correlated with coupling between frontal delta phase to motor beta amplitude. Finally, we performed a factor analysis to derive 2 symptom dimensions and found that mood symptoms positively tracked with reward-evaluation and motivation symptoms negatively tracked with goal-directed behavior. Altogether, these results provide evidence that 2 aspects of reward-based decision-making are instantiated by different modes of prefrontal top-down control and are modulated in different symptom dimensions of depression.
Keywords: cross-frequency coupling; depression; goal-directed behavior; reward-evaluation; symptom dimensions.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
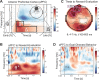
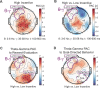
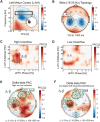
References
-
- Adcock RA, Thangavel A, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Knutson B, Gabrieli JD. 2006. Reward-motivated learning: mesolimbic activation precedes memory formation. Neuron. 50(3):507–517. - PubMed
-
- Alekseichuk I, Turi Z, de Lara GA, Antal A, Paulus W. 2016. Spatial working memory in humans depends on theta and high gamma synchronization in the prefrontal cortex. Curr Biol. 26(12):1513–1521. - PubMed
-
- Andersen SB, Moore RA, Venables L, Corr PJ. 2009. Electrophysiological correlates of anxious rumination. Int J Psychophysiol. 71(2):156–169. - PubMed
-
- Arns M, Etkin A, Hegerl U, Williams LM, DeBattista C, Palmer DM, Fitzgerald PB, Harris A, deBeuss R, Gordon E. 2015. Frontal and rostral anterior cingulate (rACC) theta EEG in depression: implications for treatment outcome? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 25(8):1190–1200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

