Has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced the oral health and nutritional status of elderly patients with digestive cancer?: A retrospective study in Fukui, Japan
- PMID: 34622884
- PMCID: PMC8500633
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027500
Has the COVID-19 pandemic influenced the oral health and nutritional status of elderly patients with digestive cancer?: A retrospective study in Fukui, Japan
Abstract
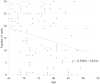
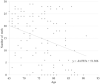
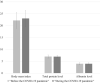
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected various aspects, including socioeconomic status and health. This retrospective study aimed to investigate the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on oral health based on the number of teeth that contribute to mastication, and the nutritional status of elderly patients with digestive cancers.The authors defined the before and during COVID-19 periods in this study as January 2019 to December 2019 and January 2020 to December 2020, respectively. Patients with digestive cancer who underwent general, laboratory, and orthopantomograph examinations for preoperative oral health assessment before general anesthesia participated in this study. The authors investigated the following general characteristics: (1) sex, (2) age, and (3) the organ affected by disease and scheduled for surgery under general anesthesia. The authors collected information about (4) the number of teeth that could contribute to mastication as a clinical oral health parameter. The parameters: (5) body mass index, (6) serum total protein levels, and (7) serum albumin levels were used to indicate the nutritional status.A total of 233 elderly patients with digestive cancer participated in this study. There was no significant difference between the age of the patients with digestive cancer. There was also no significant difference in the number of teeth that could contribute to mastication. Additionally, there was no significant difference in nutritional status as indicated by the body mass index, serum total protein levels, and serum albumin levels.This study showed that the COVID-19 pandemic during 2020 did not have a significant influence on the oral health and nutritional status of elderly patients with digestive cancer. However, the influence of COVID-19 on community oral health may become apparent in the future. Thus, dental professionals should continue further research regarding the effects of COVID-19 on oral health.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interests to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Health organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19). 2020; https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19.
-
- Bharmal N, Bailey J, Johnson V, et al. . Addressing COVID-19 health disparities through a regional community health response. Cleve Clin J Med 2021;doi: 10.3949/ccjm.88a.ccc072. - PubMed
-
- Piskorowski WA, Fitzgerald M, Mastey J, Krell RE. Development of a sustainable community-based dental education program. J Dent Educ 2011;75:1038–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

