Head-to-head evaluation of seven different seroassays including direct viral neutralisation in a representative cohort for SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34623233
- PMCID: PMC8604188
- DOI: 10.1099/jgv.0.001653
Head-to-head evaluation of seven different seroassays including direct viral neutralisation in a representative cohort for SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
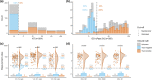
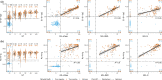
A number of seroassays are available for SARS-CoV-2 testing; yet, head-to-head evaluations of different testing principles are limited, especially using raw values rather than categorical data. In addition, identifying correlates of protection is of utmost importance, and comparisons of available testing systems with functional assays, such as direct viral neutralisation, are needed.We analysed 6658 samples consisting of true-positives (n=193), true-negatives (n=1091), and specimens of unknown status (n=5374). For primary testing, we used Euroimmun-Anti-SARS-CoV-2-ELISA-IgA/IgG and Roche-Elecsys-Anti-SARS-CoV-2. Subsequently virus-neutralisation, GeneScriptcPass, VIRAMED-SARS-CoV-2-ViraChip, and Mikrogen-recomLine-SARS-CoV-2-IgG were applied for confirmatory testing. Statistical modelling generated optimised assay cut-off thresholds. Sensitivity of Euroimmun-anti-S1-IgA was 64.8%, specificity 93.3% (manufacturer's cut-off); for Euroimmun-anti-S1-IgG, sensitivity was 77.2/79.8% (manufacturer's/optimised cut-offs), specificity 98.0/97.8%; Roche-anti-N sensitivity was 85.5/88.6%, specificity 99.8/99.7%. In true-positives, mean and median Euroimmun-anti-S1-IgA and -IgG titres decreased 30/90 days after RT-PCR-positivity, Roche-anti-N titres decreased significantly later. Virus-neutralisation was 80.6% sensitive, 100.0% specific (≥1:5 dilution). Neutralisation surrogate tests (GeneScriptcPass, Mikrogen-recomLine-RBD) were >94.9% sensitive and >98.1% specific. Optimised cut-offs improved test performances of several tests. Confirmatory testing with virus-neutralisation might be complemented with GeneScriptcPassTM or recomLine-RBD for certain applications. Head-to-head comparisons given here aim to contribute to the refinement of testing strategies for individual and public health use.
Keywords: COVID-19; RBD; SARS-CoV-2; antibody; nucleocapsid; serology; spike; virus neutralisation.
Conflict of interest statement
AW and MH report personal fees and non-financial support from Roche Diagnostics, LO reports non-financial support from Roche Diagnostics. AW, MH and LO report non-financial support from Euroimmun, non-financial support from Viramed, non-financial support from Mikrogen. AW, MH, LO report grants, non-financial support and other from German Centre for Infection Research DZIF, grants and non-financial support from Government of Bavaria, non-financial support from BMW, non-financial support from Munich Police, non-financial support and other from Accenture. JH reports grants from German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, during the conduct of the study. MH and AW report personal fees and non-financial support from Dr. Box-Betrobox, non-financial support from Dr. Becker MVZ during the conduct of the study. In addition, MH, AW, MB have a patent on a sample system for sputum diagnostics of SARS-CoV-2 pending. AW is involved in other different patents and companies not in relation with the serology of SARS-CoV-2. AW reports personal fees and other from Haeraeus Sensors, non-financial support from Bruker Daltonics, all of which are outside the submitted work, and non-related to SARS-CoV-2. MB is an authorised representative partner of Dr. Becker MVZ.
Figures
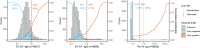



References
-
- (FIND) FfIND SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic pipeline. 2020. https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

