Guidelines on Implementing Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Korea
- PMID: 34623784
- PMCID: PMC8511380
- DOI: 10.3947/ic.2021.0098
Guidelines on Implementing Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Korea
Abstract
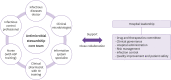
These guidelines were developed as a part of the 2021 Academic R&D Service Project of the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency in response to requests from healthcare professionals in clinical practice for guidance on developing antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs). These guidelines were developed by means of a systematic literature review and a summary of recent literature, in which evidence-based intervention methods were used to address key questions about the appropriate use of antimicrobial agents and ASP expansion. These guidelines also provide evidence of the effectiveness of ASPs and describe intervention methods applicable in Korea.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Antimicrobial stewardship program; Guidelines; Korea.
Copyright © 2021 by The Korean Society of Infectious Diseases, Korean Society for Antimicrobial Therapy, and The Korean Society for AIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- Barlam TF, Cosgrove SE, Abbo LM, MacDougall C, Schuetz AN, Septimus EJ, Srinivasan A, Dellit TH, Falck-Ytter YT, Fishman NO, Hamilton CW, Jenkins TC, Lipsett PA, Malani PN, May LS, Moran GJ, Neuhauser MM, Newland JG, Ohl CA, Samore MH, Seo SK, Trivedi KK. Implementing an antibiotic stewardship program: guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62:e51–e77. - PMC - PubMed
-
- O'Neill J. Antimicrobial resistance. Tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. [Accessed 30 August 2021]. Available at: https://wellcomecollection.org/works/rdpck35v/items.
-
- Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America; Infectious Diseases Society of America; Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society. Policy statement on antimicrobial stewardship by the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), and the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society (PIDS) Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2012;33:322–327. - PubMed
-
- Dellit TH, Owens RC, McGowan JE, Jr, Gerding DN, Weinstein RA, Burke JP, Huskins WC, Paterson DL, Fishman NO, Carpenter CF, Brennan PJ, Billeter M, Hooton TM Infectious Diseases Society of America; Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America. Infectious Diseases Society of America and the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America guidelines for developing an institutional program to enhance antimicrobial stewardship. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:159–177. - PubMed

