SHMT2 inhibition disrupts the TCF3 transcriptional survival program in Burkitt lymphoma
- PMID: 34624079
- PMCID: PMC8938936
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021012081
SHMT2 inhibition disrupts the TCF3 transcriptional survival program in Burkitt lymphoma
Abstract
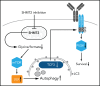
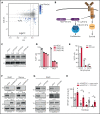
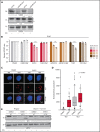
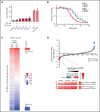
Burkitt lymphoma (BL) is an aggressive lymphoma type that is currently treated by intensive chemoimmunotherapy. Despite the favorable clinical outcome for most patients with BL, chemotherapy-related toxicity and disease relapse remain major clinical challenges, emphasizing the need for innovative therapies. Using genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 screens, we identified B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling, specific transcriptional regulators, and one-carbon metabolism as vulnerabilities in BL. We focused on serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2), a key enzyme in one-carbon metabolism. Inhibition of SHMT2 by either knockdown or pharmacological compounds induced anti-BL effects in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, SHMT2 inhibition led to a significant reduction of intracellular glycine and formate levels, which inhibited the mTOR pathway and thereby triggered autophagic degradation of the oncogenic transcription factor TCF3. Consequently, this led to a collapse of tonic BCR signaling, which is controlled by TCF3 and is essential for BL cell survival. In terms of clinical translation, we also identified drugs such as methotrexate that synergized with SHMT inhibitors. Overall, our study has uncovered the dependency landscape in BL, identified and validated SHMT2 as a drug target, and revealed a mechanistic link between SHMT2 and the transcriptional master regulator TCF3, opening up new perspectives for innovative therapies.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures






Comment in
-
Metabolic path toward TCF3 inactivation in Burkitt lymphoma.Blood. 2022 Jan 27;139(4):475-476. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014133. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35084477 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhu KY, Song KW, Connors JM, et al. Excellent real-world outcomes of adults with Burkitt lymphoma treated with CODOX-M/IVAC plus or minus rituximab. Br J Haematol. 2018;181(6):782-790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

