Entropy and complexity unveil the landscape of memes evolution
- PMID: 34625623
- PMCID: PMC8501102
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-99468-6
Entropy and complexity unveil the landscape of memes evolution
Abstract
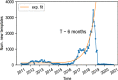
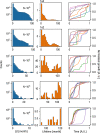
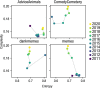
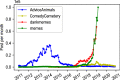
On the Internet, information circulates fast and widely, and the form of content adapts to comply with users' cognitive abilities. Memes are an emerging aspect of the internet system of signification, and their visual schemes evolve by adapting to a heterogeneous context. A fundamental question is whether they present culturally and temporally transcendent characteristics in their organizing principles. In this work, we study the evolution of 2 million visual memes published on Reddit over ten years, from 2011 to 2020, in terms of their statistical complexity and entropy. A combination of a deep neural network and a clustering algorithm is used to group memes according to the underlying templates. The grouping of memes is the cornerstone to trace the growth curve of these objects. We observe an exponential growth of the number of new created templates with a doubling time of approximately 6 months, and find that long-lasting templates are associated with strong early adoption. Notably, the creation of new memes is accompanied with an increased visual complexity of memes content, in a continuous effort to represent social trends and attitudes, that parallels a trend observed also in painting art.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sunstein CR. # republic. New York: Princeton University Press; 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

