F9 missense mutations impairing factor IX activation are associated with pleiotropic plasma phenotypes
- PMID: 34626083
- PMCID: PMC9298354
- DOI: 10.1111/jth.15552
F9 missense mutations impairing factor IX activation are associated with pleiotropic plasma phenotypes
Abstract
Background: Circulating dysfunctional factor IX (FIX) might modulate distribution of infused FIX in hemophilia B (HB) patients. Recurrent substitutions at FIX activation sites (R191-R226, >300 patients) are associated with variable FIX activity and antigen (FIXag) levels.
Objectives: To investigate the (1) expression of a complete panel of missense mutations at FIX activation sites and (2) contribution of F9 genotypes on the FIX pharmacokinetics (PK).
Methods: We checked FIX activity and antigen and activity assays in plasma and after recombinant expression of FIX variants and performed an analysis of infused FIX PK parameters in patients (n = 30), mostly enrolled in the F9 Genotype and PK HB Italian Study (GePKHIS; EudraCT ID2017-003902-42).
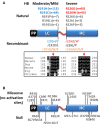
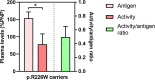
Results: The variable FIXag amounts and good relation between biosynthesis and activity of multiple R191 variants results in graded moderate-to-mild severity of the R191C>L>P>H substitutions. Recombinant expression may predict the absence in the HB mutation database of the benign R191Q/W/K and R226K substitutions. Equivalent changes at R191/R226 produced higher FIXag levels for R226Q/W/P substitutions, as also observed in p.R226W female carrier plasma. Pharmacokinetics analysis in patients suggested that infused FIX Alpha distribution and Beta elimination phases positively correlated with endogenous FIXag levels. Mean residence time was particularly prolonged (79.4 h, 95% confidence interval 44.3-114.5) in patients (n = 7) with the R191/R226 substitutions, which in regression analysis were independent predictors (β coefficient 0.699, P = .004) of Beta half-life, potentially prolonged by the increasing over time ratio between endogenous and infused FIX.
Conclusions: FIX activity and antigen levels and specific features of the dysfunctional R191/R226 variants may exert pleiotropic effects both on HB patients' phenotypes and substitutive treatment.
Keywords: factor IX activation; hemophilia B; pharmacogenetics; pharmacokinetics; recombinant proteins.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B. reports grants and personal fees from Pfizer, grants from Bayer, and grants and non‐financial support from Grifols, outside the submitted work. M.M. reports personal fees from Kedrion, Novo Nordisk, SOBI, Bayer, Bioverativ, Octapharma, CSL Behring and grants from Pfizer, outside the submitted work. A.C.M. has acted as a paid consultant to Bayer, CSL, Kedrion, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Shire, and Sobi, and as a paid invited speaker for Bayer, CSL, Novo Nordisk, Shire, and Sobi, outside the submitted work. G.C. reports personal fees from Roche, Bayer, Shire, Uniqure, Kedrion, Novo Nordisk, and Werfen; grants and personal fees from CSL Behring and Sobi; and grants from Pfizer, outside the submitted work. M.P. received grants from Novo Nordisk and Pfizer and personal fees from Pfizer, outside the submitted work. F.B. reports grants from Bayer, outside the submitted work, and the financial support of GePKHIS by an unconditioned Investigator Initiated Research grant from Pfizer. The remaining authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Monroe DM, Hoffman M. What does it take to make the perfect clot? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:41‐48. - PubMed
-
- Lesk AM, Fordham WD. Conservation and variability in the structures of serine proteinases of the chymotrypsin family. J Mol Biol. 1996;258:501‐537. - PubMed
-
- Yousef GM, Elliott MB, Kopolovic AD, Serry E, Diamandis EP. Sequence and evolutionary analysis of the human trypsin subfamily of serine peptidases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1698:77‐86. - PubMed
-
- Bajaj SP, Rapaport SI, Russell WA. Redetermination of the rate‐limiting step in the activation of factor IX by factor XIa and by factor VIIa/tissue factor. Explanation for different electrophoretic radioactivity profiles obtained on activation of 3H‐ and 125I‐labeled factor IX. Biochemistry. 1983;22:4047‐4053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

